The Roles of Cardiovascular H2-Histamine Receptors Under Normal and Pathophysiological Conditions
- PMID: 34987383
- PMCID: PMC8720924
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.732842
The Roles of Cardiovascular H2-Histamine Receptors Under Normal and Pathophysiological Conditions
Abstract
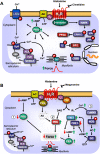
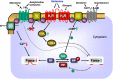
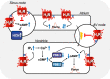
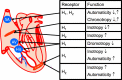
This review addresses pharmacological, structural and functional relationships among H2-histamine receptors and H1-histamine receptors in the mammalian heart. The role of both receptors in the regulation of force and rhythm, including their electrophysiological effects on the mammalian heart, will then be discussed in context. The potential clinical role of cardiac H2-histamine-receptors in cardiac diseases will be examined. The use of H2-histamine receptor agonists to acutely increase the force of contraction will be discussed. Special attention will be paid to the potential role of cardiac H2-histamine receptors in the genesis of cardiac arrhythmias. Moreover, novel findings on the putative role of H2-histamine receptor antagonists in treating chronic heart failure in animal models and patients will be reviewed. Some limitations in our biochemical understanding of the cardiac role of H2-histamine receptors will be discussed. Recommendations for further basic and translational research on cardiac H2-histamine receptors will be offered. We will speculate whether new knowledge might lead to novel roles of H2-histamine receptors in cardiac disease and whether cardiomyocyte specific H2-histamine receptor agonists and antagonists should be developed.
Keywords: H2 histamine receptor; arrhythmias; contractil effect; heart failure; ischemia - reperfusion.
Copyright © 2021 Neumann, Kirchhefer, Dhein, Hofmann and Gergs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ackermann D., Kutscher F. (1910). Untersuchungen über die physiologische Wirkung einer Secalebase und des Imidazolyäthylamins. Z. für Biologie 54, 387–394.
-
- Ackermann D. (1910). Über den bakteriellen Abbau des Histidins. Hoppe-Seyler´s Z. für physiologische Chem. 65, 504–510. 10.1515/bchm2.1910.65.5-6.504 - DOI
-
- Akaishi Y., Hattori Y., Yoshimoto K., Kitabatake A., Yasuda K., Kanno M. (2000). Involvement of Tyrosine Phosphorylation in the Positive Inotropic Effect Produced by H(1)-receptors with Histamine in guinea-pig Left Atrium. Br. J. Pharmacol. 130 (4), 907–915. 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703355 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

