Effect of dose, dosing intervals, and hypoxic stress on the reversal of pulmonary hypertension by mesenchymal stem cell extracellular vesicles
- PMID: 34987768
- PMCID: PMC8723172
- DOI: 10.1177/20458940211046137
Effect of dose, dosing intervals, and hypoxic stress on the reversal of pulmonary hypertension by mesenchymal stem cell extracellular vesicles
Abstract
Rationale: Mesenchymal stem cell extracellular vesicles (MSC EVs) reverse pulmonary hypertension, but little information is available regarding what dose is effective and how often it needs to be given. This study examined the effects of dose reduction and use of longer dosing intervals and the effect of hypoxic stress of MSC prior to EV collection.
Methods: Adult male rats with pulmonary hypertension induced by Sugen 5416 and three weeks of hypoxia (SuHx-pulmonary hypertension) were injected with MSC EV or phosphate buffered saline the day of removal from hypoxia using one of the following protocols: (1) Once daily for three days at doses of 0.2, 1, 5, 20, and 100 µg/kg, (2) Once weekly (100 µg/kg) for five weeks, (3) Once every other week (100 µg/kg) for 10 weeks, (4) Once daily (20 µg/kg) for three days using EV obtained from MSC exposed to 48 h of hypoxia (HxEV) or MSC kept in normoxic conditions (NxEV).
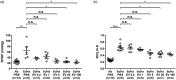
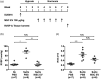
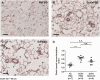
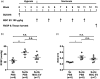
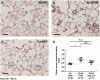
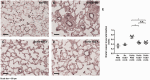
Main results: MSC EV reversed increases in right ventricular systolic pressure (RVSP), right ventricular to left ventricle + septum weight (RV/LV+S), and muscularization index of pulmonary vessels ≤50 µm when given at doses of 20 or 100 μg/kg. RVSP, RV/LV+S, and muscularization index were significantly higher in SuHx-pulmonary hypertension rats treated once weekly with phosphate buffered saline for five weeks or every other week for 10 weeks than in normoxic controls, but not significantly increased in SuHx-pulmonary hypertension rats given MSC EV. Both NxEV and HxEV significantly reduced RVSP, RV/LV+S, and muscularization index, but no differences were seen between treatment groups.
Conclusions: MSC EV are effective at reversing SuHx-pulmonary hypertension when given at lower doses and longer dosing intervals than previously reported. Hypoxic stress does not enhance the efficacy of MSC EV at reversing pulmonary hypertension. These findings support the feasibility of MSC EV as a long-term treatment for pulmonary hypertension.
Keywords: exosomes; pulmonary vascular remodeling; right ventricular hypertrophy.
© The Author(s) 2021.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cell Extracellular Vesicles Reverse Sugen/Hypoxia Pulmonary Hypertension in Rats.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2020 May;62(5):577-587. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2019-0154OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31721618 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic effects of hypoxia-preconditioned bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells and their extracellular vesicles in experimental pulmonary arterial hypertension.Life Sci. 2023 Sep 15;329:121988. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2023.121988. Epub 2023 Jul 29. Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 37517581
-
Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stromal cells exert a therapeutic effect on hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension by modulating the YAP1/SPP1 signaling pathway.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Dec;168:115816. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115816. Epub 2023 Nov 2. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 37918254
-
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes ameliorate hypoxic pulmonary hypertension by inhibiting the Hsp90aa1/ERK/pERK pathway.Biochem Pharmacol. 2024 Aug;226:116382. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2024.116382. Epub 2024 Jun 21. Biochem Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38909785
-
Bone Marrow Endothelial Progenitor Cells Are the Cellular Mediators of Pulmonary Hypertension in the Murine Monocrotaline Injury Model.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017 Jul;6(7):1595-1606. doi: 10.1002/sctm.16-0386. Epub 2017 May 5. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017. PMID: 28474513 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Therapy for Pulmonary Hypertension: A Comprehensive Review of Preclinical Studies.J Interv Cardiol. 2022 Nov 4;2022:5451947. doi: 10.1155/2022/5451947. eCollection 2022. J Interv Cardiol. 2022. PMID: 36419957 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Cellular and Molecular Effects of Fetoscopic Endoluminal Tracheal Occlusion in Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia.Front Pediatr. 2022 Jul 5;10:925106. doi: 10.3389/fped.2022.925106. eCollection 2022. Front Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 35865706 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel insights into the potential applications of stem cells in pulmonary hypertension therapy.Respir Res. 2024 Jun 7;25(1):237. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-02865-4. Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 38849894 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Benza RL, Miller DP, Barst RJ, et al.. An evaluation of long-term survival from time of diagnosis in pulmonary arterial hypertension from the REVEAL Registry. Chest 2012; 142: 448–456. - PubMed
-
- Gebler A, Zabel O, Seliger B. The immunomodulatory capacity of mesenchymal stem cells. Trends Mol Med 2012; 18: 128–1–34.. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

