Targeting Metabolic Pathways of Myeloid Cells Improves Cancer Immunotherapy
- PMID: 34988072
- PMCID: PMC8721007
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.747863
Targeting Metabolic Pathways of Myeloid Cells Improves Cancer Immunotherapy
Abstract
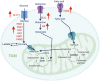
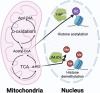
Tumor-infiltrating myeloid cells are a prominent pro-tumorigenic immune cell population that limit host anti-tumor immunity and present a significant obstacle for many cancer immunotherapies. Targeting the mechanisms regulating myeloid cell function within the tumor microenvironment may overcome immunotherapy resistance in some cancers. Recent discoveries in the emerging field of immunometabolism reveal that the metabolic profiles of intratumoral myeloid cells are rewired to adapt to the nutrition-limited tumor microenvironment, and this shapes their pro-tumor phenotypes. Interestingly, metabolic modulation can shift these myeloid cells toward the immune-stimulating anti-tumor phenotype. In this review, we will highlight the roles of specific metabolic pathways in the activation and function of myeloid cells, and discuss the therapeutic value of metabolically reprogramming myeloid cells to augment and improve outcomes with cancer immunotherapy.
Keywords: immunometabolism; immunotherapy; myeloid cells; myeloid-derived suppressor cells; tumor-associated dendritic cells; tumor-associated macrophages; tumor-associated neutrophils; tumor-infiltrating myeloid cells.
Copyright © 2021 Li, Bolyard, Xin and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Arts R. J. W., Plantinga T. S., Tuit S., Ulas T., Heinhuis B., Tesselaar M., et al. (2016). Transcriptional and Metabolic Reprogramming Induce an Inflammatory Phenotype in Non-medullary Thyroid Carcinoma-Induced Macrophages. Oncoimmunology 5, e1229725. 10.1080/2162402x.2016.1229725 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bingisser R. M., Tilbrook P. A., Holt P. G., Kees U. R. (1998). Macrophage-derived Nitric Oxide Regulates T Cell Activation via Reversible Disruption of the Jak3/STAT5 Signaling Pathway. J. Immunol. 160, 5729–5734. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

