Machine Learning Based Prediction of COVID-19 Mortality Suggests Repositioning of Anticancer Drug for Treating Severe Cases
- PMID: 34988543
- PMCID: PMC8677630
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ailsci.2021.100020
Machine Learning Based Prediction of COVID-19 Mortality Suggests Repositioning of Anticancer Drug for Treating Severe Cases
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "Machine Learning Based Prediction of COVID-19 Mortality Suggests Repositioning of Anticancer Drug for Treating Severe Cases"[Artificial Intelligence in Life Sciences] 1(2021), 100020.Artif Intell Life Sci. 2022 Dec;2:100032. doi: 10.1016/j.ailsci.2022.100032. Epub 2022 Feb 8. Artif Intell Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35156080 Free PMC article.
Abstract
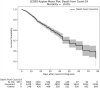
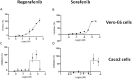
Despite available vaccinations COVID-19 case numbers around the world are still growing, and effective medications against severe cases are lacking. In this work, we developed a machine learning model which predicts mortality for COVID-19 patients using data from the multi-center 'Lean European Open Survey on SARS-CoV-2-infected patients' (LEOSS) observational study (>100 active sites in Europe, primarily in Germany), resulting into an AUC of almost 80%. We showed that molecular mechanisms related to dementia, one of the relevant predictors in our model, intersect with those associated to COVID-19. Most notably, among these molecules was tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2), a protein that has been patented as drug target in Alzheimer's Disease but also genetically associated with severe COVID-19 outcomes. We experimentally verified that anti-cancer drugs Sorafenib and Regorafenib showed a clear anti-cytopathic effect in Caco2 and VERO-E6 cells and can thus be regarded as potential treatments against COVID-19. Altogether, our work demonstrates that interpretation of machine learning based risk models can point towards drug targets and new treatment options, which are strongly needed for COVID-19.
Keywords: Covid19; Drug repositioning; Explainable ai; Machine learning; Precision medicine.
© 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Akiba Takuya, et al. Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, KDD ’19. Association for Computing Machinery; New York, NY, USA: 2019. Optuna: a Next-Generation Hyperparameter Optimization Framework; pp. 2623–2631. September 30, 2021. - DOI
-
- Algassim Abdulrahman A., et al. Prognostic Significance of Hemoglobin Level and Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia in SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Ann. Hematol. 2020 https://www.meta.org/papers/prognostic-significance-of-hemoglobin-level-... November 21, 2021. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ali Rashid, et al. Isaric 4c Mortality Score As A Predictor Of In-Hospital Mortality In Covid-19 Patients Admitted In Ayub Teaching Hospital During First Wave Of The Pandemic. Journal of Ayub Medical College, Abbottabad: JAMC. 2021;33(1):20–25. - PubMed
-
- Ansems Kelly, et al. Remdesivir for the Treatment of COVID-19′. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2021;(8) https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cdsr/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD014962/full October 18, 2021. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
