Clinico-radiological features, molecular spectrum, and identification of prognostic factors in developmental and epileptic encephalopathy due to inosine triphosphate pyrophosphatase (ITPase) deficiency
- PMID: 34989426
- PMCID: PMC9152572
- DOI: 10.1002/humu.24326
Clinico-radiological features, molecular spectrum, and identification of prognostic factors in developmental and epileptic encephalopathy due to inosine triphosphate pyrophosphatase (ITPase) deficiency
Abstract
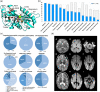
Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 35 (DEE 35) is a severe neurological condition caused by biallelic variants in ITPA, encoding inosine triphosphate pyrophosphatase, an essential enzyme in purine metabolism. We delineate the genotypic and phenotypic spectrum of DEE 35, analyzing possible predictors for adverse clinical outcomes. We investigated a cohort of 28 new patients and reviewed previously described cases, providing a comprehensive characterization of 40 subjects. Exome sequencing was performed to identify underlying ITPA pathogenic variants. Brain MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scans were systematically analyzed to delineate the neuroradiological spectrum. Survival curves according to the Kaplan-Meier method and log-rank test were used to investigate outcome predictors in different subgroups of patients. We identified 18 distinct ITPA pathogenic variants, including 14 novel variants, and two deletions. All subjects showed profound developmental delay, microcephaly, and refractory epilepsy followed by neurodevelopmental regression. Brain MRI revision revealed a recurrent pattern of delayed myelination and restricted diffusion of early myelinating structures. Congenital microcephaly and cardiac involvement were statistically significant novel clinical predictors of adverse outcomes. We refined the molecular, clinical, and neuroradiological characterization of ITPase deficiency, and identified new clinical predictors which may have a potentially important impact on diagnosis, counseling, and follow-up of affected individuals.
Keywords: ITPA; ITPase; congenital microcephaly; developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 35; heart disease; white matter abnormalities.
© 2022 The Authors. Human Mutation published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Teresa Santiago‐Sim, Amy Dameron, and Hui Yang are employees of GeneDx, Inc. The remaining authors declare that there are no conflict of interests.
Figures

References
-
- Abolhassani, N. , Iyama, T. , Tsuchimoto, D. , Sakumi, K. , Ohno, M. , Behmanesh, M. , & Nakabeppu, Y. (2010). NUDT16 and ITPA play a dual protective role in maintaining chromosome stability and cell growth by eliminating dIDP/IDP and dITP/ITP from nucleotide pools in mammals. Nucleic Acids Research, 38, 2891–2903. 10.1093/nar/gkp1250 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

