Tracking cell lineages in 3D by incremental deep learning
- PMID: 34989675
- PMCID: PMC8741210
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.69380
Tracking cell lineages in 3D by incremental deep learning
Abstract
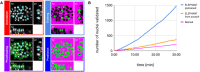
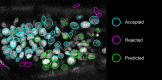
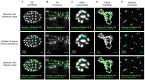
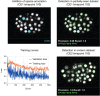
Deep learning is emerging as a powerful approach for bioimage analysis. Its use in cell tracking is limited by the scarcity of annotated data for the training of deep-learning models. Moreover, annotation, training, prediction, and proofreading currently lack a unified user interface. We present ELEPHANT, an interactive platform for 3D cell tracking that addresses these challenges by taking an incremental approach to deep learning. ELEPHANT provides an interface that seamlessly integrates cell track annotation, deep learning, prediction, and proofreading. This enables users to implement cycles of incremental learning starting from a few annotated nuclei. Successive prediction-validation cycles enrich the training data, leading to rapid improvements in tracking performance. We test the software's performance against state-of-the-art methods and track lineages spanning the entire course of leg regeneration in a crustacean over 1 week (504 timepoints). ELEPHANT yields accurate, fully-validated cell lineages with a modest investment in time and effort.
Keywords: cell lineage; cell tracking; deep learning; developmental biology; regeneration.
© 2022, Sugawara et al.
Conflict of interest statement
KS, MA KS is employed part-time by LPIXEL Inc, ÇÇ No competing interests declared
Figures








References
-
- Cicek O, Abdulkadir A, Lienkamp SS, Brox T, Ronneberger O. In: Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention - MICCAI 2016. Ourselin S, Joskowicz L, Sabuncu MR, Unal G, Wells W, editors. Springer International Publishing; 2016. 3D U-Net: Learning Dense Volumetric Segmentation from Sparse Annotation. - DOI
-
- Crocker JC, Grier DG. Methods of Digital Video Microscopy for Colloidal Studies. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science. 1996;179:298–310. doi: 10.1006/jcis.1996.0217. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

