Virtual reality biofeedback interventions for treating anxiety : A systematic review, meta-analysis and future perspective
- PMID: 34989862
- PMCID: PMC8825383
- DOI: 10.1007/s00508-021-01991-z
Virtual reality biofeedback interventions for treating anxiety : A systematic review, meta-analysis and future perspective
Abstract
Background: Virtual reality (VR)-based biofeedback is a relatively new intervention and is increasingly being used for the treatment of anxiety disorders. This is the first research synthesis regarding effects and efficacy of this novel mode of treatment.
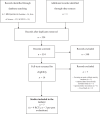
Method: We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of the VR biofeedback literature on treating anxiety symptoms. The MEDLINE/PubMed, Scopus and Web of Science databases were searched for eligible pre-post comparisons and randomized controlled trials (RCTs). We used self-reported anxiety, heart rate (HR), and heart rate variability (HRV) as primary outcome measures.
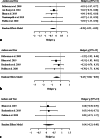
Results: A total of 7 studies with 191 participants reported VR biofeedback interventions. Of these studies 5 were RCTs, with 103 participants receiving VR biofeedback and 99 control participants (either 2D biofeedback or waiting list controls). We found that VR biofeedback significantly lowers self-reported anxiety (g = -0.28) and HR (g = -0.45), but not HRV. Furthermore, there were no significant differences in outcomes between VR biofeedback and 2D biofeedback but a significant reduction in HR in the VR biofeedback group compared with the waiting list (g = -0.52).
Conclusion: While the first findings are optimistic, more controlled studies with a wider variety of samples are needed to bring this field forward. Particularly, children and adolescents may profit from the combination of gamification elements, VR, and biofeedback.
Keywords: Anxiety; Complementary therapies; Heart rate variability; Psychological treatment; Virtual environment.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
O.D. Kothgassner, A. Goreis, I. Bauda, A. Ziegenaus, L.M. Glenk and A. Felnhofer declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Virtual Reality Biofeedback in Health: A Scoping Review.Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback. 2022 Mar;47(1):1-15. doi: 10.1007/s10484-021-09529-9. Epub 2021 Dec 3. Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback. 2022. PMID: 34860290 Free PMC article.
-
Designing and developing a nature-based virtual reality with heart rate variability biofeedback for surgical anxiety and pain management: evidence from total knee arthroplasty patients.Aging Ment Health. 2024 May;28(5):738-753. doi: 10.1080/13607863.2023.2270442. Epub 2023 Oct 18. Aging Ment Health. 2024. PMID: 37850735 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of virtual reality-based biofeedback for depressive and anxiety symptoms: Randomized controlled study.J Affect Disord. 2024 Sep 15;361:392-398. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2024.06.031. Epub 2024 Jun 15. J Affect Disord. 2024. PMID: 38885844 Clinical Trial.
-
The effect of heart rate variability biofeedback training on stress and anxiety: a meta-analysis.Psychol Med. 2017 Nov;47(15):2578-2586. doi: 10.1017/S0033291717001003. Epub 2017 May 8. Psychol Med. 2017. PMID: 28478782
-
Systematic Review of Biofeedback Interventions for Addressing Anxiety and Depression in Children and Adolescents with Long-Term Physical Conditions.Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback. 2018 Sep;43(3):179-192. doi: 10.1007/s10484-018-9399-z. Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback. 2018. PMID: 29946920
Cited by
-
Cutting-Edge Physical Therapy in Mechanical Circulatory Support: Critical Care Physical Therapy Perspectives.Tex Heart Inst J. 2023 Jul 17;50(4):e238180. doi: 10.14503/THIJ-23-8180. Tex Heart Inst J. 2023. PMID: 37470248 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Cancer patients' acceptance of virtual reality interventions for self-emotion regulation.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 9;15(1):12185. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-95160-1. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40204807 Free PMC article.
-
Virtual Reality Respiratory Biofeedback in an Outpatient Pediatric Pain Rehabilitation Program: Mixed Methods Pilot Study.JMIR Rehabil Assist Technol. 2025 Apr 14;12:e66352. doi: 10.2196/66352. JMIR Rehabil Assist Technol. 2025. PMID: 40228293 Free PMC article.
-
A Smartphone-Gamified Virtual Reality Exposure Therapy Augmented With Biofeedback for Ailurophobia: Development and Evaluation Study.JMIR Serious Games. 2024 Mar 6;12:e34535. doi: 10.2196/34535. JMIR Serious Games. 2024. PMID: 38446522 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Restorative Environment and Presence on Anxiety and Depression Based on Interactive Virtual Reality Scenarios.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Jun 27;19(13):7878. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19137878. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35805535 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. Washington: American Psychiatric Association Publishing; 2013.
-
- Appelhans BM, Luecken LJ. Heart rate variability as an index of regulated emotional responding. Rev Gen Psychol. 2006;10(3):229–240.
-
- Bandelow B, Sagebiel A, Belz M, et al. Enduring effects of psychological treatments for anxiety disorders: meta-analysis of follow-up studies. Br J Psychiatry. 2018;212(6):333–338. - PubMed
-
- Baxter AJ, Scott KM, Vos T, Whiteford HA. Global prevalence of anxiety disorders: a systematic review and meta-regression. Psychol Med. 2013;43(5):897–910. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

