The Purkinje-myocardial junction is the anatomic origin of ventricular arrhythmia in CPVT
- PMID: 34990403
- PMCID: PMC8855823
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.151893
The Purkinje-myocardial junction is the anatomic origin of ventricular arrhythmia in CPVT
Abstract
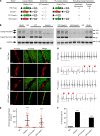
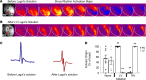
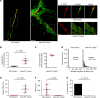
Catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (CPVT) is an arrhythmia syndrome caused by gene mutations that render RYR2 Ca release channels hyperactive, provoking spontaneous Ca release and delayed afterdepolarizations (DADs). What remains unknown is the cellular source of ventricular arrhythmia triggered by DADs: Purkinje cells in the conduction system or ventricular cardiomyocytes in the working myocardium. To answer this question, we used a genetic approach in mice to knock out cardiac calsequestrin either in Purkinje cells or in ventricular cardiomyocytes. Total loss of calsequestrin in the heart causes a severe CPVT phenotype in mice and humans. We found that loss of calsequestrin only in ventricular myocytes produced a full-blown CPVT phenotype, whereas mice with loss of calsequestrin only in Purkinje cells were comparable to WT mice. Subendocardial chemical ablation or restoration of calsequestrin expression in subendocardial cardiomyocytes neighboring Purkinje cells was sufficient to protect against catecholamine-induced arrhythmias. In silico modeling demonstrated that DADs in ventricular myocardium can trigger full action potentials in the Purkinje fiber, but not vice versa. Hence, ectopic beats in CPVT are likely generated at the Purkinje-myocardial junction via a heretofore unrecognized tissue mechanism, whereby DADs in the ventricular myocardium trigger full action potentials in adjacent Purkinje cells.
Keywords: Arrhythmias; Calcium signaling; Cardiology; Genetic diseases.
Figures



References
-
- Postma AV, et al. Absence of calsequestrin 2 causes severe forms of catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia. Circ Res. 2002;91(8):e21–e26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- F32 HL140874/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK058404/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R35 HL144980/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA068485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM152284/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL151223/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- F30 HL145917/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK059637/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 NS007491/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL146107/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 EY008126/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105983/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007347/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

