Clonal hematopoiesis in sickle cell disease
- PMID: 34990411
- PMCID: PMC8843701
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI156060
Clonal hematopoiesis in sickle cell disease
Abstract
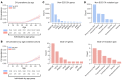
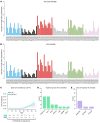
BACKGROUNDCurative gene therapies for sickle cell disease (SCD) are currently undergoing clinical evaluation. The occurrence of myeloid malignancies in these trials has prompted safety concerns. Individuals with SCD are predisposed to myeloid malignancies, but the underlying causes remain undefined. Clonal hematopoiesis (CH) is a premalignant condition that also confers significant predisposition to myeloid cancers. While it has been speculated that CH may play a role in SCD-associated cancer predisposition, limited data addressing this issue have been reported.METHODSHere, we leveraged 74,190 whole-genome sequences to robustly study CH in SCD. Somatic mutation calling methods were used to assess CH in all samples and comparisons between individuals with and without SCD were performed.RESULTSWhile we had sufficient power to detect a greater than 2-fold increased rate of CH, we found no detectable variation in rate or clone properties between individuals affected by SCD and controls. The rate of CH in individuals with SCD was unaltered by hydroxyurea use.CONCLUSIONSWe did not observe an increased risk for acquiring detectable CH in SCD, at least as measured by whole-genome sequencing. These results should help guide ongoing efforts and further studies that seek to better define the risk factors underlying myeloid malignancy predisposition in SCD and help ensure that curative therapies can be more safely applied.FUNDINGNew York Stem Cell Foundation and the NIH.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00492531.
Keywords: Hematology; Leukemias.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
The hematopoietic saga of clonality in sickle cell disease.J Clin Invest. 2022 Mar 1;132(5):e158251. doi: 10.1172/JCI158251. J Clin Invest. 2022. PMID: 35175224 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Science. Gene Therapy Trials for Sickle Cell Disease Halted After Two Patients Develop Cancer. https://www.sciencemag.org/news/2021/02/gene-therapy-trials-sickle-cell-... Updated February 16, 2021. Accessed May 7, 2021.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
- HHSN268201100037C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL066987/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR048797/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- F32 HL085989/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL067348/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201800001C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK103794/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL117626/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL148050/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL092301/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007574/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DP5 OD029586/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL120393/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL120393/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG058921/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS058700/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HG000040/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500015C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500016C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500014C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR007122/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL146500/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL093093/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK071891/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States

