Serum miR-34a-5p and miR-199a-3p as new biomarkers of neonatal sepsis
- PMID: 34990478
- PMCID: PMC8735601
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0262339
Serum miR-34a-5p and miR-199a-3p as new biomarkers of neonatal sepsis
Abstract
Background: Neonatal sepsis is a serious condition. Recent clinical studies have indicated that microRNAs (miRNAs) are key players in the pathogenesis of sepsis, which could be used as biomarkers for this condition.
Patients and methods: A total of 90 neonates with sepsis and 90 healthy neonates were enrolled in this study. qRT-PCR was performed to measure the expression levels of serum miR-34a-5p and miR-199a-3p.
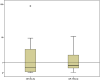
Results: miR-34a-5p and miR-199a-3p serum levels were significantly reduced in neonates with sepsis compared with those in healthy neonates (P = 0.006 and P = 0.001, respectively). Significant correlations of miR-34a-5p and miR-199a-3p with each of TLC, RDW, RBS, and C-reactive protein (CRP) as well as SNAPII were observed, indicating their associations with the severity of neonatal sepsis.
Conclusion: miR-34a-5p and miR-199a-3p may be useful as novel biomarkers in neonatal sepsis and may provide a new direction for its treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Satar M, Ozlü F. Neonatal sepsis: a continuing disease burden. Turk J Pediatr. 2012. Sep-Oct;54(5):449–57. . - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

