Argonaute-2 protects the neurovascular unit from damage caused by systemic inflammation
- PMID: 34991639
- PMCID: PMC8740421
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-021-02324-7
Argonaute-2 protects the neurovascular unit from damage caused by systemic inflammation
Abstract
Background: The brain vasculature plays a pivotal role in the inflammatory process by modulating the interaction between blood cells and the neurovascular unit. Argonaute-2 (Ago2) has been suggested as essential for endothelial survival but its role in the brain vasculature or in the endothelial-glial crosstalk has not been addressed. Thus, our aim was to clarify the significance of Ago2 in the inflammatory responses elicited by these cell types.
Methods: Mouse primary cultures of brain endothelial cells, astrocytes and microglia were used to evaluate cellular responses to the modulation of Ago2. Exposure of microglia to endothelial cell-conditioned media was used to assess the potential for in vivo studies. Adult mice were injected intraperitoneally with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) (2 mg/kg) followed by three daily intraperitoneal injections of Ago2 (0.4 nM) to assess markers of endothelial disruption, glial reactivity and neuronal function.
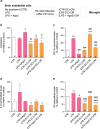
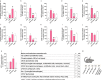
Results: Herein, we demonstrated that LPS activation disturbed the integrity of adherens junctions and downregulated Ago2 in primary brain endothelial cells. Exogenous treatment recovered intracellular Ago2 above control levels and recuperated vascular endothelial-cadherin expression, while downregulating LPS-induced nitric oxide release. Primary astrocytes did not show a significant change in Ago2 levels or response to the modulation of the Ago2 system, although endogenous Ago2 was shown to be critical in the maintenance of tumor necrosis factor-α basal levels. LPS-activated primary microglia overexpressed Ago2, and Ago2 silencing contained the inflammatory response to some extent, preventing interleukin-6 and nitric oxide release. Moreover, the secretome of Ago2-modulated brain endothelial cells had a protective effect over microglia. The intraperitoneal injection of LPS impaired blood-brain barrier and neuronal function, while triggering inflammation, and the subsequent systemic administration of Ago2 reduced or normalized endothelial, glial and neuronal markers of LPS damage. This outcome likely resulted from the direct action of Ago2 over the brain endothelium, which reestablished glial and neuronal function.
Conclusions: Ago2 could be regarded as a putative therapeutic agent, or target, in the recuperation of the neurovascular unit in inflammatory conditions.
Keywords: Argonaute-2; Brain endothelial cells; Glia; Lipopolysaccharide; Neuroprotection; Secretome.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing or conflicting interests.
Figures

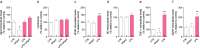
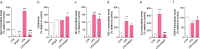


Similar articles
-
Paroxetine suppresses reactive microglia-mediated but not lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in primary astrocytes.J Neuroinflammation. 2020 Feb 5;17(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s12974-020-1712-0. J Neuroinflammation. 2020. PMID: 32024542 Free PMC article.
-
TSG-6 in conditioned media from adipose mesenchymal stem cells protects against visual deficits in mild traumatic brain injury model through neurovascular modulation.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019 Nov 5;10(1):318. doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1436-1. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31690344 Free PMC article.
-
Novel celecoxib analogues inhibit glial production of prostaglandin E2, nitric oxide, and oxygen radicals reverting the neuroinflammatory responses induced by misfolded prion protein fragment 90-231 or lipopolysaccharide.Pharmacol Res. 2016 Nov;113(Pt A):500-514. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2016.09.010. Epub 2016 Sep 22. Pharmacol Res. 2016. PMID: 27667770
-
Foe or friend? Janus-faces of the neurovascular unit in the formation of brain metastases.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2018 Apr;38(4):563-587. doi: 10.1177/0271678X17732025. Epub 2017 Sep 18. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2018. PMID: 28920514 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Expanding Cell Diversity of the Brain Vasculature.Front Physiol. 2020 Dec 3;11:600767. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.600767. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 33343397 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Argonaute 2 restored erectile function and corpus cavernosum mitochondrial function by reducing apoptosis in a mouse model of cavernous nerve injury.Investig Clin Urol. 2024 Jul;65(4):400-410. doi: 10.4111/icu.20240077. Investig Clin Urol. 2024. PMID: 38978220 Free PMC article.
-
Argonaute 2 Restores Erectile Function by Enhancing Angiogenesis and Reducing Reactive Oxygen Species Production in Streptozotocin (STZ)-Induced Type-1 Diabetic Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 2;24(3):2935. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032935. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36769259 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Varatharaj A, Galea I. The blood-brain barrier in systemic inflammation. Brain Behav Immun. 2017;60:1–12. - PubMed
-
- Machado-Pereira M, Santos T, Bernardino L, Ferreira R. Vascular inter-regulation of inflammation: molecular and cellular targets for CNS therapy. J Neurochem. 2016;140(5):692–702. - PubMed
-
- Dauphinee SM, Karsan A. Lipopolysaccharide signaling in endothelial cells. Lab Investig. 2006;86(1):9–22. - PubMed
-
- Akira S, Takeda K. Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4:499–511. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

