Role of Fcγ receptors in HER2-targeted breast cancer therapy
- PMID: 34992090
- PMCID: PMC8739678
- DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2021-003171
Role of Fcγ receptors in HER2-targeted breast cancer therapy
Abstract
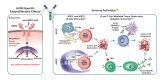
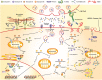
Several therapeutic monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), including those targeting epidermal growth factor receptor, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2), and CD20, mediate fragment crystallizable gamma receptor (FcγR)-dependent activities as part of their mechanism of action. These activities include induction of antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) and antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis (ADCP), which are innate immune mechanisms of cancer cell elimination. FcγRs are distinguished by their affinity for the Fc fragment, cell distribution, and type of immune response they induce. Activating FcγRIIIa (CD16A) on natural killer cells plays a crucial role in mediating ADCC, and activating FcγRIIa (CD32A) and FcγRIIIa on macrophages are important for mediating ADCP. Polymorphisms in FcγRIIIa and FcγRIIa generate variants that bind to the Fc portion of antibodies with different affinities. This results in differential FcγR-mediated activities associated with differential therapeutic outcomes across multiple clinical settings, from early stage to metastatic disease, in patients with HER2+ breast cancer treated with the anti-HER2 mAb trastuzumab. Trastuzumab has, nonetheless, revolutionized HER2+ breast cancer treatment, and several HER2-directed mAbs have been developed using Fc glyco-engineering or Fc protein-engineering to enhance FcγR-mediated functions. An example of an approved anti-HER2 Fc-engineered chimeric mAb is margetuximab, which targets the same epitope as trastuzumab, but features five amino acid substitutions in the IgG 1 Fc domain that were deliberately introduced to increase binding to activating FcγRIIIa and decrease binding to inhibitory FcγRIIb (CD32B). Margetuximab enhances Fc-dependent ADCC in vitro more potently than the combination of pertuzumab (another approved mAb directed against an alternate HER2 epitope) and trastuzumab. Margetuximab administration also enhances HER2-specific B cell and T cell-mediated responses ex vivo in samples from patients treated with prior lines of HER2 antibody-based therapies. Stemming from these observations, a worthwhile future goal in the treatment of HER2+ breast cancer is to promote combinatorial approaches that better eradicate HER2+ cancer cells via enhanced immunological mechanisms.
Keywords: adaptive immunity; breast neoplasms; immunity; innate; review.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: AM reports grants from Roche and Eisai; personal fees from MacroGenics, Roche, Eisai, Novartis, and Lilly; participation in advisory boards from MacroGenics, Roche, Eisai, Novartis, Lilly. WJG has nothing to disclose. HSR reports personal fees for short-term consulting from Puma and Samsung; institutional grants for clinical research study activities from MacroGenics, Roche, Pfizer, Novartis, Lilly, Merck, Seattle Genetics, Odonate Therapeutics, Eisai, Sermonix, and Immunomedics, Daiichi Sankyo. MDP reports personal consulting fees from MacroGenics, AstraZeneca/Daiichi Sankyo, Pfizer, and Roche/Genentech, and grant support on this topic from the Parker Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy and the Mary Kay Foundation. JLN is an employee of MacroGenics. EPR was an employee of MacroGenics and is now an employee of Partner Therapeutics. FA was an employee of MacroGenics and is now an employee of AstraZeneca.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
