Real-Life Clinical Data of Lenvatinib versus Sorafenib for Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Italy
- PMID: 34992463
- PMCID: PMC8713715
- DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S330195
Real-Life Clinical Data of Lenvatinib versus Sorafenib for Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Italy
Abstract
Background: Lenvatinib has been approved in Italy since October 2019 as a first-line therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and to date data on effectiveness and safety of lenvatinib are not available in our region. To fill this gap, we performed a multicentric analysis of the real-world treatment outcomes with the propensity score matching in a cohort of Italian patients with unresectable HCC who were treated with either sorafenib or lenvatinib.
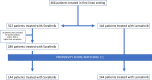
Aims and methods: To evaluate the effectiveness of sorafenib and lenvatinib as primary treatment of advanced HCC in clinical practice we performed a multicentric analysis of the treatment outcomes of 288 such patients recruited in 11 centers in Italy. A propensity score was used to mitigate confounding due to referral biases in the assessment of mortality and progression-free survival.
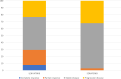
Results: Over a follow-up period of 11 months the Cox regression model showed 48% reduction of death risk for patients treated with lenvatinib (95% CI: 0.34-0.81; p = 0.0034), compared with those treated with sorafenib. The median PFS was 9.0 and 4.9 months for lenvatinib and sorafenib arm, respectively. Patients treated with lenvatinib showed a higher percentage of response rate (29.4% vs 2.8%; p < 0.00001) compared with patients treated with sorafenib. Sorafenib was shown to be correlated with more HFSR, diarrhea and fatigue, while lenvatinib with more hypertension and fatigue.
Conclusion: Our study highlighted for the first time the efficacy and safety of lenvatinib in an Italian cohort of patients.
Keywords: hepatocarcinoma; lenvatinib; sorafenib.
© 2021 Burgio et al.
Conflict of interest statement
ACG: Speaking/teaching, consultant and advisory board for Bayer, AstraZeneca, BMS, Ipsen, MSD, EISAI. MI: Speaking/teaching, consultant and advisory board for Bayer, Gilead Sciences, BMS, Janssen, Ipsen, MSD, BTG-Boston Scientific, AbbVie, Guerbet, EISAI, Shionogi. FM: Consultant for and travel grants from Bayer, consultant for EISAI/Merck and Ipsen, during the conduct of the study; consultant for Menarini, Novo Nordisk, Astra Zeneca, Allergan, and Novartis, travel grants from AbbVie. MI: personal fees from IPSEN, during the conduct of the study. FP: advisory board, consultant/lectures from Bracco, Bayer, Astra Zeneca, IPSEN, Roche, Eisai, MSD, Esaote, GE, Samsung, Exact Sciences, Tiziana Life Sciences. CC: personal fees from Eisai, Ipsen. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

