Clinical Epidemiology, Risk Factors, and Control Strategies of Klebsiella pneumoniae Infection
- PMID: 34992583
- PMCID: PMC8724557
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.750662
Clinical Epidemiology, Risk Factors, and Control Strategies of Klebsiella pneumoniae Infection
Abstract
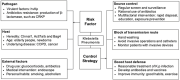
Klebsiella species cause infections at multiple sites, including lung, urinary tract, bloodstream, wound or surgical site, and brain. These infections are more likely to occur in people with preexisting health conditions. Klebsiella pneumoniae (K. pneumoniae) has emerged as a major pathogen of international concern due to the increasing incidences of hypervirulent and carbapenem-resistant strains. It is imperative to understand risk factors, prevention strategies, and therapeutic avenues to treat multidrug-resistant Klebsiella infections. Here, we highlight the epidemiology, risk factors, and control strategies against K. pneumoniae infections to highlight the grave risk posed by this pathogen and currently available options to treat Klebsiella-associated diseases.
Keywords: CRKP; Klebsiella pneumoniae; clinical epidemiology; control strategies; hvKp; risk factors.
Copyright © 2021 Chang, Sharma, Dela Cruz and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Baron E. J., Miller J. M., Weinstein M. P., Richter S. S., Gilligan P. H., Thomson R. B., et al. (2013). A guide to utilization of the microbiology laboratory for diagnosis of infectious diseases: 2013 recommendations by the infectious diseases society of America (IDSA) and the American society for microbiology (ASM) a. Clin. Infect. Dis. 57, e22–e121. doi: 10.1093/cid/cit278, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources