Nanomaterials for Remediation of Environmental Pollutants
- PMID: 34992641
- PMCID: PMC8727162
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/1764647
Nanomaterials for Remediation of Environmental Pollutants
Abstract
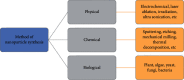
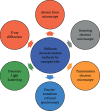
Today, environmental contamination is a big concern for both developing and developed countries. The primary sources of contamination of land, water, and air are extensive industrialization and intense agricultural activities. Various traditional methods are available for the treatment of different pollutants in the environment, but all have some limitations. Due to this, an alternative method is required which is effective and less toxic and provides better outcomes. Nanomaterials have attracted a lot of interest in terms of environmental remediation. Because of their huge surface area and related high reactivity, nanomaterials perform better in environmental clean-up than other conventional approaches. They can be modified for specific uses to provide novel features. Due to the large surface-area-to-volume ratio and the presence of a larger number of reactive sites, nanoscale materials can be extremely reactive. These characteristics allow for higher interaction with contaminants, leading to a quick reduction of contaminant concentration. In the present review, an overview of different nanomaterials that are potential in the remediation of environmental pollutants has been discussed.
Copyright © 2021 Arpita Roy et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Adeleye A. S., Conway J. R., Garner K., Huang Y., Su Y., Keller A. A. Engineered nanomaterials for water treatment and remediation: costs, benefits, and applicability. Chemical Engineering Journal . 2016;286:640–662.
-
- Roy A., Bharadvaja N. Efficient removal of heavy metals from artificial wastewater using biochar. Environmental Nanotechnology, Monitoring & Management . 2021;16 doi: 10.1016/j.enmm.2021.100602.100602 - DOI
-
- Roy A., Elzaki A., Tirth V., et al. Biological synthesis of nanocatalysts and their applications. Catalysts . 2021;11(12):p. 1494. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-92111-2_1. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources