Excitonic transport driven by repulsive dipolar interaction in a van der Waals heterostructure
- PMID: 34992677
- PMCID: PMC7612161
- DOI: 10.1038/s41566-021-00908-6
Excitonic transport driven by repulsive dipolar interaction in a van der Waals heterostructure
Abstract
Dipolar bosonic gases are currently the focus of intensive research due to their interesting many-body physics in the quantum regime. Their experimental embodiments range from Rydberg atoms to GaAs double quantum wells and van der Waals heterostructures built from transition metal dichalcogenides. Although quantum gases are very dilute, mutual interactions between particles could lead to exotic many-body phenomena such as Bose-Einstein condensation and high-temperature superfluidity. Here, we report the effect of repulsive dipolar interactions on the dynamics of interlayer excitons in the dilute regime. By using spatial and time-resolved photoluminescence imaging, we observe the dynamics of exciton transport, enabling a direct estimation of the exciton mobility. The presence of interactions significantly modifies the diffusive transport of excitons, effectively acting as a source of drift force and enhancing the diffusion coefficient by one order of magnitude. The repulsive dipolar interactions combined with the electrical control of interlayer excitons opens up appealing new perspectives for excitonic devices.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
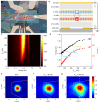
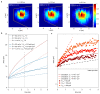
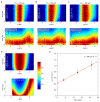
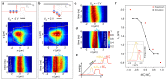
References
-
- Rivera P, et al. Observation of long-lived interlayer excitons in monolayer MoSe2-WSe2 heterostructures. Nat Commun. 2015;6:6242. - PubMed
-
- Unuchek D, et al. Room-temperature electrical control of exciton flux in a van der Waals heterostructure. Nature. 2018;560:340–344. - PubMed
-
- High AA, Hammack AT, Butov LV, Hanson M, Gossard AC. Exciton optoelectronic transistor. Opt Lett. 2007;32:2466–2468. - PubMed
-
- High AA, Novitskaya EE, Butov LV, Hanson M, Gossard AC. Control of Exciton Fluxes in an Excitonic Integrated Circuit. Science. 2008;321:229–231. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
