Unexpected discovery of prostatic diffuse large B-cell lymphoma after thulium laser vaporization in a patient with Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia
- PMID: 34993124
- PMCID: PMC8666792
- DOI: 10.21037/qims-20-1319
Unexpected discovery of prostatic diffuse large B-cell lymphoma after thulium laser vaporization in a patient with Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://dx.doi.org/10.21037/qims-20-1319). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
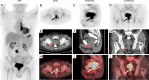
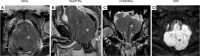
References
-
- Jiménez C, Alonso-Álvarez S, Alcoceba M, Ordóñez GR, García-Álvarez M, Prieto-Conde MI, Chillón MC, Balanzategui A, Corral R, Marín LA, Gutiérrez NC, Puig N, Sarasquete ME, González M, García-Sanz R. From Waldenström's macroglobulinemia to aggressive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a whole-exome analysis of abnormalities leading to transformation. Blood Cancer J 2017;7:e591. 10.1038/bcj.2017.72 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Treon SP, Xu L, Yang G, Zhou Y, Liu X, Cao Y, Sheehy P, Manning RJ, Patterson CJ, Tripsas C, Arcaini L, Pinkus GS, Rodig SJ, Sohani AR, Harris NL, Laramie JM, Skifter DA, Lincoln SE, Hunter ZR. MYD88 L265P somatic mutation in Waldenström's macroglobulinemia. N Engl J Med 2012;367:826-33. 10.1056/NEJMoa1200710 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
