Genetic Factors Associated with Prostate Cancer Conversion from Active Surveillance to Treatment
- PMID: 34993496
- PMCID: PMC8725988
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xhgg.2021.100070
Genetic Factors Associated with Prostate Cancer Conversion from Active Surveillance to Treatment
Abstract
Men diagnosed with low-risk prostate cancer (PC) are increasingly electing active surveillance (AS) as their initial management strategy. While this may reduce the side effects of treatment for prostate cancer, many men on AS eventually convert to active treatment. PC is one of the most heritable cancers, and genetic factors that predispose to aggressive tumors may help distinguish men who are more likely to discontinue AS. To investigate this, we undertook a multi-institutional genome-wide association study (GWAS) of 5,222 PC patients and 1,139 other patients from replication cohorts, all of whom initially elected AS and were followed over time for the potential outcome of conversion from AS to active treatment. In the GWAS we detected 18 variants associated with conversion, 15 of which were not previously associated with PC risk. With a transcriptome-wide association study (TWAS), we found two genes associated with conversion (MAST3, p = 6.9×10-7 and GAB2, p = 2.0×10-6). Moreover, increasing values of a previously validated 269-variant genetic risk score (GRS) for PC was positively associated with conversion (e.g., comparing the highest to the two middle deciles gave a hazard ratio [HR] = 1.13; 95% Confidence Interval [CI]= 0.94-1.36); whereas, decreasing values of a 36-variant GRS for prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels were positively associated with conversion (e.g., comparing the lowest to the two middle deciles gave a HR = 1.25; 95% CI, 1.04-1.50). These results suggest that germline genetics may help inform and individualize the decision of AS-or the intensity of monitoring on AS-versus treatment for the initial management of patients with low-risk PC.
Keywords: genetics; genome-wide association study; prostate; prostatic neoplasms.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
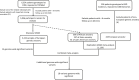
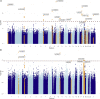
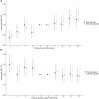
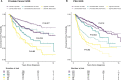
References
-
- Mohler J.L., Antonarakis E.S., Armstrong A.J., D’Amico A.V., Davis B.J., Dorff T., Eastham J.A., Enke C.A., Farrington T.A., Higano C.S., et al. Prostate Cancer, Version 2.2019, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Canc. Netw. 2019;17:479–505. - PubMed
-
- Parikh R.B., Robinson K.W., Chhatre S., Medvedeva E., Cashy J.P., Veera S., Bauml J.M., Fojo T., Navathe A.S., Malkowicz S.B., et al. Comparison by Race of Conservative Management for Low-Risk and Intermediate-Risk Prostate Cancers in Veterans From 2004 to 2018. JAMA Netw. Open. 2020;3:e2018318. - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

