Siglec-F Promotes IL-33-Induced Cytokine Release from Bone Marrow-Derived Eosinophils Independently of the ITIM and ITIM-like Motif Phosphorylation
- PMID: 34996839
- PMCID: PMC8852812
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.2100184
Siglec-F Promotes IL-33-Induced Cytokine Release from Bone Marrow-Derived Eosinophils Independently of the ITIM and ITIM-like Motif Phosphorylation
Abstract
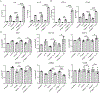
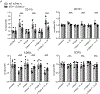
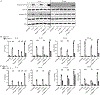
Eosinophils are potent innate effector cells associated mainly with type 2 immune responses elicited by helminths and allergens. Their activity needs to be tightly controlled to prevent severe inflammation and tissue damage. Eosinophil degranulation and secretion of inflammatory effector molecules, including cytokines, chemokines, and lipid mediators, can be regulated by activating and inhibitory receptors on the cell surface. In this study, we investigated the modulation of proliferation, apoptosis, gene expression, and cytokine/chemokine secretion from IL-33-activated Mus musculus eosinophils on cross-linking of the transmembrane receptor Sialic acid-binding Ig-like lectin F (Siglec-F). Siglec-F contains an ITIM plus an ITIM-like motif in its intracellular tail and is mainly regarded as an inhibitory and apoptosis-inducing receptor. In vitro costimulation of bone marrow-derived eosinophils with anti-Siglec-F and IL-33 compared with treatment with either alone led to enhanced STAT6 phosphorylation, stronger induction of hypoxia/glycolysis-related proinflammatory genes, and elevated secretion of type 2 cytokines (IL-4, IL-13) and chemokines (CCL3, CCL4) with only minor effects on proliferation and apoptosis. Using a competitive mixed bone marrow chimera approach with wild-type and Siglec-F-deficient eosinophils, we observed no evidence for Siglec-F-regulated inhibition of Aspergillus fumigatus-elicited lung eosinophilia. Truncation of the Siglec-F cytoplasmic tail, but not mutation of the ITIM and ITIM-like motifs, ablated the effect of enhanced cytokine/chemokine secretion. This provides evidence for an ITIM phosphorylation-independent signaling pathway from the cytoplasmic tail of the Siglec-F receptor that enhances effector molecule release from activated eosinophils.
Copyright © 2022 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures
B.S.B. receives remuneration for serving on the scientific advisory board of Allakos, Inc. and owns stock in Allakos. B.S.B. is a co-inventor on existing Siglec-8–related patents and thus may be entitled to a share of royalties received by Johns Hopkins University during development and potential sales of such products. B.S.B is also a co-founders of Allakos, Inc. which makes him subject to certain restrictions under University policy. The terms of this arrangement are being managed by Johns Hopkins University and Northwestern University in accordance with their conflict of interest policies. The remaining authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase (PI3K) Orchestrates Aspergillus fumigatus-Induced Eosinophil Activation Independently of Canonical Toll-Like Receptor (TLR)/C-Type-Lectin Receptor (CLR) Signaling.mBio. 2022 Aug 30;13(4):e0123922. doi: 10.1128/mbio.01239-22. Epub 2022 Jun 13. mBio. 2022. PMID: 35695427 Free PMC article.
-
Sialyltransferase ST3Gal-III regulates Siglec-F ligand formation and eosinophilic lung inflammation in mice.J Immunol. 2013 Jun 15;190(12):5939-48. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1203455. Epub 2013 May 15. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23677475 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous airway mucins carry glycans that bind Siglec-F and induce eosinophil apoptosis.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015 May;135(5):1329-1340.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2014.10.027. Epub 2014 Dec 12. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25497369 Free PMC article.
-
Siglec-8 on human eosinophils and mast cells, and Siglec-F on murine eosinophils, are functionally related inhibitory receptors.Clin Exp Allergy. 2009 Mar;39(3):317-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2008.03173.x. Clin Exp Allergy. 2009. PMID: 19178537 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sensing the neuronal glycocalyx by glial sialic acid binding immunoglobulin-like lectins.Neuroscience. 2014 Sep 5;275:113-24. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.05.061. Epub 2014 Jun 9. Neuroscience. 2014. PMID: 24924144 Review.
Cited by
-
Inflammatory cytokine signalling in vulvovaginal candidiasis: a hot mess driving immunopathology.Oxf Open Immunol. 2024 Aug 17;5(1):iqae010. doi: 10.1093/oxfimm/iqae010. eCollection 2024. Oxf Open Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39234208 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interleukin-33: Metabolic checkpoints, metabolic processes, and epigenetic regulation in immune cells.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 1;13:900826. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.900826. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35979357 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Eosinophils in inflammatory bowel disease pathogenesis: an ROS-centric view.Front Allergy. 2025 Aug 8;6:1608202. doi: 10.3389/falgy.2025.1608202. eCollection 2025. Front Allergy. 2025. PMID: 40860650 Free PMC article.
-
Siglecs in allergy and asthma.Mol Aspects Med. 2023 Apr;90:101104. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2022.101104. Epub 2022 Jul 11. Mol Aspects Med. 2023. PMID: 35835621 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of eosinophil recruitment and heterogeneity during allergic airway inflammation.Front Allergy. 2025 Apr 10;6:1585142. doi: 10.3389/falgy.2025.1585142. eCollection 2025. Front Allergy. 2025. PMID: 40276331 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tateno H, Crocker PR, and Paulson JC. 2005. Mouse Siglec-F and human Siglec-8 are functionally convergent paralogs that are selectively expressed on eosinophils and recognize 6’-sulfo-sialyl Lewis X as a preferred glycan ligand. Glycobiology 15: 1125–1135. - PubMed
-
- Angata T, Hingorani R, Varki NM, and Varki A. 2001. Cloning and characterization of a novel mouse Siglec, mSiglec-F: differential evolution of the mouse and human (CD33) Siglec-3-related gene clusters. J Biol Chem 276: 45128–45136. - PubMed
-
- Zhang JQ, Biedermann B, Nitschke L, and Crocker PR. 2004. The murine inhibitory receptor mSiglec-E is expressed broadly on cells of the innate immune system whereas mSiglec-F is restricted to eosinophils. Eur J Immunol 34: 1175–1184. - PubMed
-
- Nutku E, Aizawa H, Hudson SA, and Bochner BS. 2003. Ligation of Siglec-8: a selective mechanism for induction of human eosinophil apoptosis. Blood 101: 5014–5020. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

