A randomized trial to determine the minimum effective lidocaine volume for median nerve block using hydrodissection
- PMID: 34996918
- PMCID: PMC8742045
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-03660-7
A randomized trial to determine the minimum effective lidocaine volume for median nerve block using hydrodissection
Abstract
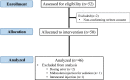
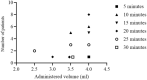
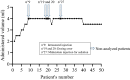
Ultrasound-guided hydrodissection with 5% dextrose in water (DW5) creates a peri-nervous compartment, separating the nerve from the neighboring anatomical structures. The aim of this randomized study was to determine the minimum volume of lidocaine 2% with epinephrine 1:200,000 required when using this technique to achieve an effective median nerve block at the elbow in 95% of patients (MEAV95). Fifty-two patients scheduled for elective hand surgery received an ultrasound-guided circumferential perineural injection of 4 ml DW5 and an injection of local anesthetic (LA) following a biased coin up-and-down sequential allocation method. A successful block was defined as a light touch completely suppressed on the two distal phalanges of the index finger within a 30-min evaluation period. The MEAV95 of lidocaine 2% with epinephrine was 4 ml [IQR 3.5-4.0]. Successful median nerve block was obtained in 38 cases (82.6%) with median onset time of 20.0 [10.0-21.2] minutes (95% CI 15-20). The analgesia duration was 248 [208-286] minutes (95% CI 222-276). Using an ultrasound-guided hydrodissection technique with DW5, the MEAV95 to block the median nerve at the elbow with 2% lidocaine with epinephrine was 4 ml [IQR 3.5-4.0]. This volume is close to that usually recommended in clinical practice.Trial registration clinicaltrials.gov. NCT02438657, Date of registration: May 8, 2015.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ultrasound-guided perineural circumferential median nerve block with and without prior dextrose 5% hydrodissection: a prospective randomized double-blinded noninferiority trial.Anesth Analg. 2012 Sep;115(3):728-33. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e31825fa37d. Epub 2012 Jun 28. Anesth Analg. 2012. PMID: 22745114 Clinical Trial.
-
Minimum effective volume of combined lidocaine-bupivacaine for analgesic subparaneural popliteal sciatic nerve block.Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2014 Mar-Apr;39(2):108-11. doi: 10.1097/AAP.0000000000000051. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2014. PMID: 24496169 Clinical Trial.
-
An ultrasonographic assessment of nerve stimulation-guided median nerve block at the elbow: a local anesthetic spread, nerve size, and clinical efficacy study.Anesth Analg. 2010 Aug;111(2):561-7. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e3181e3a06f. Epub 2010 Jul 7. Anesth Analg. 2010. PMID: 20610551
-
[Peribulbar anesthesia versus retrobulbar anesthesia with facial nerve block. Techniques, local anesthetics and additives, akinesia and sensory block, complications].Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 1994 Feb;204(2):75-89. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1035503. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 1994. PMID: 8170098 Review. German.
-
Ultrasound-Guided Nerve Hydrodissection for Pain Management: Rationale, Methods, Current Literature, and Theoretical Mechanisms.J Pain Res. 2020 Aug 4;13:1957-1968. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S247208. eCollection 2020. J Pain Res. 2020. PMID: 32801851 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ultrasound-Guided Nerve Blocks Improve Success Rate of Closed Reduction of Colles' Fractures: A Randomised Controlled Trial.Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2025 Jul;69(6):e70063. doi: 10.1111/aas.70063. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2025. PMID: 40536436 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Gitman M, Barrington MJ. Local anesthetic systemic toxicity: A review of recent case reports and registries. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2018;43:124–130. - PubMed
-
- Ponrouch M, et al. Estimation and pharmacodynamic consequences of the minimum effective anesthetic volumes for median and ulnar nerve blocks: A randomized, double-blind, controlled comparison between ultrasound and nerve stimulation guidance. Anesth. Analg. 2010;111:1059–1064. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e3181eb6372. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

