Improvement of the affinity of an anti-rat P2X4 receptor antibody by introducing electrostatic interactions
- PMID: 34996944
- PMCID: PMC8742113
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-03784-w
Improvement of the affinity of an anti-rat P2X4 receptor antibody by introducing electrostatic interactions
Abstract
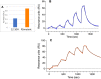
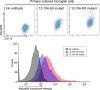
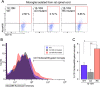
We have recently developed a mouse monoclonal antibody (12-10H) binding to the head domain region in rat P2X4 receptor (rP2X4R, which is crucial for the pathogenesis of neuropathic pain) expressed on the cell with the highest binding affinity (KD = 20 nM). However, the 12-10H antibody failed to detect endogenously expressed P2X4Rs in microglia isolated from the spinal cord of rats whose spinal nerves were injured. Then, we prepared R5 mutant, in which five arginine residues were introduced into variable regions except for the "hot spot" in the 12-10H antibody to increase electrostatic interactions with the head domain, an anionic region, in rP2X4R. The mutation resulted in an increase of 50-fold in the affinity of the R5 mutant for the head domain with respect to the intact 12-10H antibody. As a result, detection of P2X4Rs endogenously expressed on primary cultured microglial cells originated from the neonatal rat brain and spinal cord microglia isolated from a rat model of neuropathic pain was achieved. These findings suggest a strategy to improve the affinity of a monoclonal antibody for an anionic antigen by the introduction of several arginine residues into variable regions other than the "hot spot" in the paratope.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- JP26293129/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science
- JP26293129/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science
- JP26293129/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science
- JP16H02420, JP19H05766, and JP20H02531/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science
- JP16H02420, JP19H05766, and JP20H02531/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science
- JP26293129/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science
- JP21am0101091/Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development
- JP21am0101091/Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development
- JP21am0101091/Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development
- JP18am0101094j, JP18dm0107064h, JP18mk0101081h, JP18fm0208030h, JP18fk0108073h, and JP18ak0101100h/Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development
- JP18am0101094j, JP18dm0107064h, JP18mk0101081h, JP18fm0208030h, JP18fk0108073h, and JP18ak0101100h/Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development
- JP21am0101091/Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development
- JP21am0101091/Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development
- JPMJCR20H8/the JST CREST
- JPMJCR20H8/the JST CREST
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

