Genome-wide identification and characterization of functionally relevant microsatellite markers from transcription factor genes of Tea (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze)
- PMID: 34996959
- PMCID: PMC8742041
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-03848-x
Genome-wide identification and characterization of functionally relevant microsatellite markers from transcription factor genes of Tea (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze)
Abstract
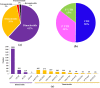
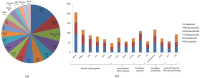
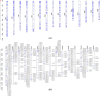
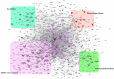
Tea, being one of the most popular beverages requires large set of molecular markers for genetic improvement of quality, yield and stress tolerance. Identification of functionally relevant microsatellite or simple sequence repeat (SSR) marker resources from regulatory "Transcription factor (TF) genes" can be potential targets to expedite molecular breeding efforts. In current study, 2776 transcripts encoding TFs harbouring 3687 SSR loci yielding 1843 flanking markers were identified from traits specific transcriptome resource of 20 popular tea cultivars. Of these, 689 functionally relevant SSR markers were successfully validated and assigned to 15 chromosomes (Chr) of CSS genome. Interestingly, 589 polymorphic markers including 403 core-set of TF-SSR markers amplified 2864 alleles in key TF families (bHLH, WRKY, MYB-related, C2H2, ERF, C3H, NAC, FAR1, MYB and G2-like). Their significant network interactions with key genes corresponding to aroma, quality and stress tolerance suggests their potential implications in traits dissection. Furthermore, single amino acid repeat reiteration in CDS revealed presence of favoured and hydrophobic amino acids. Successful deployment of markers for genetic diversity characterization of 135 popular tea cultivars and segregation in bi-parental population suggests their wider utility in high-throughput genotyping studies in tea.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Weber JL. Informativeness of human (dC-dA)n. (dG-dT)n polymorphisms. Genomics. 1990;7:524–530. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

