Phenethylamine is a substrate of monoamine oxidase B in the paraventricular thalamic nucleus
- PMID: 34996979
- PMCID: PMC8742005
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-03885-6
Phenethylamine is a substrate of monoamine oxidase B in the paraventricular thalamic nucleus
Abstract
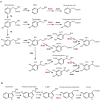
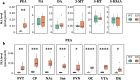
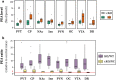
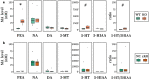
Monoamine oxidase (MAO) is a key enzyme responsible for the degradation of neurotransmitters and trace amines. MAO has two subtypes (MAO-A and MAO-B) that are encoded by different genes. In the brain, MAO-B is highly expressed in the paraventricular thalamic nucleus (PVT); however, its substrate in PVT remains unclear. To identify the MAO-B substrate in PVT, we generated Maob knockout (KO) mice and measured five candidate substrates (i.e., noradrenaline, dopamine, 3-methoxytyramine, serotonin, and phenethylamine [PEA]) by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. We showed that only PEA levels were markedly elevated in the PVT of Maob KO mice. To exclude the influence of peripheral MAO-B deficiency, we developed brain-specific Maob KO mice, finding that PEA in the PVT was increased in brain-specific Maob KO mice, whereas the extent of PEA increase was less than that in global Maob KO mice. Given that plasma PEA levels were elevated in global KO mice, but not in brain-specific KO mice, and that PEA passes across the blood-brain barrier, the substantial accumulation of PEA in the PVT of Maob KO mice was likely due to the increase in plasma PEA. These data suggest that PEA is a substrate of MAO-B in the PVT as well as other tissues.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Behavioral disinhibition and reduced anxiety-like behaviors in monoamine oxidase B-deficient mice.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2009 Dec;34(13):2746-57. doi: 10.1038/npp.2009.118. Epub 2009 Aug 26. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2009. PMID: 19710633 Free PMC article.
-
Brain injury and inflammation genes common to a number of neurological diseases and the genes involved in the genesis of GABAnergic neurons are altered in monoamine oxidase B knockout mice.Brain Res. 2022 Jan 1;1774:147724. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2021.147724. Epub 2021 Nov 12. Brain Res. 2022. PMID: 34780749 Free PMC article.
-
MAO-A and -B gene knock-out mice exhibit distinctly different behavior.Neurobiology (Bp). 1999;7(2):235-46. Neurobiology (Bp). 1999. PMID: 10591056 Review.
-
Role of MAO A and B in neurotransmitter metabolism and behavior.Pol J Pharmacol. 1999 Jan-Feb;51(1):25-9. Pol J Pharmacol. 1999. PMID: 10389141 Review.
-
Neurotransmitter selection by monoamine oxidase isoforms, dissected in terms of functional groups by mixed double mutant cycles.Org Biomol Chem. 2019 Oct 21;17(39):8871-8877. doi: 10.1039/c9ob01558b. Epub 2019 Sep 26. Org Biomol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31556440
Cited by
-
The SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein interacts with MAO-B and impairs mitochondrial energetics.Curr Res Neurobiol. 2023 Oct 6;5:100112. doi: 10.1016/j.crneur.2023.100112. eCollection 2023. Curr Res Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 38020812 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative in vitro-to-in vivo extrapolation of human adrenergic and trace amine-associated receptor 1 potencies of pre-workout supplement ingredients using physiologically based kinetic modelling-based reverse dosimetry.Arch Toxicol. 2025 May;99(5):1999-2021. doi: 10.1007/s00204-025-03992-7. Epub 2025 Apr 3. Arch Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40178592 Free PMC article.
-
Elucidating the monoamine oxidase B inhibitory effect of kaurene diterpenoids from Xylopia aethiopica: An in silico approach.PLoS One. 2024 Nov 27;19(11):e0308021. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0308021. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. Retraction in: PLoS One. 2025 May 8;20(5):e0324095. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0324095. PMID: 39602408 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Rumors of Psychedelics, Psychotropics and Related Derivatives in Vachellia and Senegalia in Contrast with Verified Records in Australian Acacia.Plants (Basel). 2022 Dec 2;11(23):3356. doi: 10.3390/plants11233356. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36501395 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yang HY, Neff NH. Beta-phenylethylamine: A specific substrate for type B monoamine oxidase of brain. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1973;187:365–371. - PubMed
-
- Fowler CJ, Tipton KF. On the substrate specificities of the two forms of monoamine oxidase. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1984;36:111–115. - PubMed
-
- Luque JM, Kwan S-W, Abell CW, Prada MD, Richards JG. Cellular expression of mRNAs encoding monoamine oxidases A and B in the rat central nervous system. J. Comp. Neurol. 1995;363:665–680. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

