Corticosterone-mediated regulation and functions of miR-218-5p in rat brain
- PMID: 34996981
- PMCID: PMC8742130
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-03863-y
Corticosterone-mediated regulation and functions of miR-218-5p in rat brain
Abstract
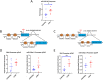
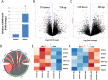
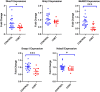
Chronic stress is one of the key precipitating factors in major depressive disorder (MDD). Stress associated studies have underscored the mechanistic role of epigenetic master players like microRNAs (miRNAs) in depression pathophysiology at both preclinical and clinical levels. Previously, we had reported changes in miR-218-5p expression in response to corticosterone (CORT) induced chronic stress. MiR-218-5p was one of the most significantly induced miRNAs in the prefrontal cortex (PFC) of rats under chronic stress. In the present report, we have investigated how chronic CORT exposure mechanistically affected miR-218-5p expression in the rat brain and how miR-218 could trigger molecular changes on its downstream regulatory pathways. Elevated expression of miR-218-5p was found in the PFC of CORT-treated rats. A glucocorticoid receptor (GR) targeted Chromatin-Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay revealed high GR occupancy on the promoter region of Slit3 gene hosting miR-218-2 in its 3rd intron. RNA-sequencing data based on RNA Induced silencing Complex Immunoprecipitation (RISC-IP) with AGO2 in SH-SY5Y cells detected six consistent target genes of miR-218-5p (APOL4, DTWD1, BNIP1, METTL22, SNAPC1, and HDAC6). The expression of all five genes, except APOL4, was successfully validated with qPCR in CORT-treated rat PFC. Further, Hdac6-based ChIP-seq experiment helped in mapping major genomic loci enriched for intergenic regions in the PFC of CORT-treated rat. A proximity-based gene ontology (GO) analysis revealed a majority of the intergenic sites to be part of key genes implicated in central nervous system functions, notably synapse organization, neuron projection morphogenesis, and axonogenesis. Our results suggest that the upregulation of miR-218-5p in PFC of CORT-treated rats possibly resulted from GR biding in the promoter region of Slit3 gene. Interestingly, Hdac6 was one of the consistent target genes potentially found to regulate CNS related genes by chromatin modification. Collectively, these findings establish the role of miR-218-5p in chronic stress and the epigenetic function it plays to induce chromatin-based transcriptional changes of several CNS genes in triggering stress-induced disorders, including depression. This also opens up the scope to understand the role of miR-218-5p as a potential target for noncoding RNA therapeutics in clinical depression.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Chronic corticosterone-mediated dysregulation of microRNA network in prefrontal cortex of rats: relevance to depression pathophysiology.Transl Psychiatry. 2015 Nov 17;5(11):e682. doi: 10.1038/tp.2015.175. Transl Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 26575223 Free PMC article.
-
HPOB, an HDAC6 inhibitor, attenuates corticosterone-induced injury in rat adrenal pheochromocytoma PC12 cells by inhibiting mitochondrial GR translocation and the intrinsic apoptosis pathway.Neurochem Int. 2016 Oct;99:239-251. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2016.08.004. Epub 2016 Aug 12. Neurochem Int. 2016. PMID: 27522966
-
Effect of hesperidin on CORT-induced apoptosis and oxidative stress of mouse hippocampal nerve cells by up-regulating miR-146a-5p.Pak J Pharm Sci. 2020 May;33(3(Special)):1383-1388. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2020. PMID: 33361027
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
-
An insight into the sprawling microverse of microRNAs in depression pathophysiology and treatment response.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2023 Mar;146:105040. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2023.105040. Epub 2023 Jan 10. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2023. PMID: 36639069 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Physical Enrichment Triggers Brain Plasticity and Influences Blood Plasma Circulating miRNA in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss).Biology (Basel). 2022 Jul 22;11(8):1093. doi: 10.3390/biology11081093. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35892949 Free PMC article.
-
microRNA-dependent regulation of gene expression in GABAergic interneurons.Front Cell Neurosci. 2023 May 5;17:1188574. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2023.1188574. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37213213 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hippocampal miR-124 Participates in the Pathogenesis of Depression via Regulating the Expression of BDNF in a Chronic Social Defeat Stress Model of Depression.Curr Neurovasc Res. 2022;19(2):210-218. doi: 10.2174/1567202619666220713105306. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2022. PMID: 35838216
-
Effects of particulate air pollution exposure on lung-brain axis and related miRNAs modulation in mouse models.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Mar 20;13:1526424. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1526424. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40248351 Free PMC article. Review.
-
METTL Family in Healthy and Disease.Mol Biomed. 2024 Aug 19;5(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s43556-024-00194-y. Mol Biomed. 2024. PMID: 39155349 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

