Cryopreservation of Anopheles stephensi embryos
- PMID: 34997079
- PMCID: PMC8741979
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-04113-x
Cryopreservation of Anopheles stephensi embryos
Abstract
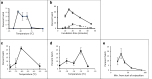
The ability to cryopreserve mosquitoes would revolutionize work on these vectors of major human infectious diseases by conserving stocks, new isolates, lab-bred strains, and transgenic lines that currently require continuous life cycle maintenance. Efforts over several decades to develop a method for cryopreservation have, until now, been fruitless: we describe here a method for the cryopreservation of Anopheles stephensi embryos yielding hatch rates of ~ 25%, stable for > 5 years. Hatched larvae developed into fertile, fecund adults and blood-fed females, produced fully viable second generation eggs, that could be infected with Plasmodium falciparum at high intensities. The key components of the cryopreservation method are: embryos at 15-30 min post oviposition, two incubation steps in 100% deuterated methanol at - 7 °C and - 14.5 °C, and rapid cooling. Eggs are recovered by rapid warming with concomitant dilution of cryoprotectant. Eggs of genetically modified A. stephensi and of A. gambiae were also successfully cryopreserved. This enabling methodology will allow long-term conservation of mosquitoes as well as acceleration of genetic studies and facilitation of mass storage of anopheline mosquitoes for release programs.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
ERJ: Patent pending US2020/041854, International Publication Number: WO/2021/011503. YW, JO, KP, SMcT, SM, AE, SLH, PFB: No competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Shililu JI, et al. Development and survival of Anopheles gambiae eggs in drying soil: influence of the rate of drying, egg age, and soil type. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 2004;20:243–247. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

