Drosophila septin interacting protein 1 regulates neurogenesis in the early developing larval brain
- PMID: 34997175
- PMCID: PMC8742078
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-04474-3
Drosophila septin interacting protein 1 regulates neurogenesis in the early developing larval brain
Abstract
Neurogenesis in the Drosophila central brain progresses dynamically in order to generate appropriate numbers of neurons during different stages of development. Thus, a central challenge in neurobiology is to reveal the molecular and genetic mechanisms of neurogenesis timing. Here, we found that neurogenesis is significantly impaired when a novel mutation, Nuwa, is induced at early but not late larval stages. Intriguingly, when the Nuwa mutation is induced in neuroblasts of olfactory projection neurons (PNs) at the embryonic stage, embryonic-born PNs are generated, but larval-born PNs of the same origin fail to be produced. Through molecular characterization and transgenic rescue experiments, we determined that Nuwa is a loss-of-function mutation in Drosophila septin interacting protein 1 (sip1). Furthermore, we found that SIP1 expression is enriched in neuroblasts, and RNAi knockdown of sip1 using a neuroblast driver results in formation of small and aberrant brains. Finally, full-length SIP1 protein and truncated SIP1 proteins lacking either the N- or C-terminus display different subcellular localization patterns, and only full-length SIP1 can rescue the Nuwa-associated neurogenesis defect. Taken together, these results suggest that SIP1 acts as a crucial factor for specific neurogenesis programs in the early developing larval brain.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
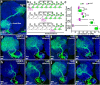
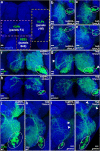
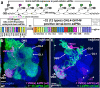

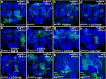
Similar articles
-
Clueless regulates aPKC activity and promotes self-renewal cell fate in Drosophila lgl mutant larval brains.Dev Biol. 2013 Sep 15;381(2):353-64. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2013.06.031. Epub 2013 Jul 5. Dev Biol. 2013. PMID: 23835532
-
Notch regulates the generation of diverse cell types from the lateral lineage of Drosophila antennal lobe.J Neurogenet. 2010 Mar;24(1):42-53. doi: 10.3109/01677060903582202. J Neurogenet. 2010. PMID: 20148759
-
Sequential activation of transcriptional repressors promotes progenitor commitment by silencing stem cell identity genes.Elife. 2020 Nov 26;9:e56187. doi: 10.7554/eLife.56187. Elife. 2020. PMID: 33241994 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of neural stem cell self-renewal and differentiation by transgenic RNAi in Drosophila.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2013 Jun;534(1-2):38-43. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2012.08.003. Epub 2012 Aug 13. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2013. PMID: 22906721 Review.
-
Growth and Maturation in Development: A Fly's Perspective.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 13;21(4):1260. doi: 10.3390/ijms21041260. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32070061 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

