Effect of positioning on blood pressure measurement in pregnancy
- PMID: 34998224
- PMCID: PMC8959067
- DOI: 10.1016/j.preghy.2021.12.013
Effect of positioning on blood pressure measurement in pregnancy
Abstract
Blood pressure is the key vital sign to detecting hypertensive disorders in pregnancy. The importance of taking blood pressure properly was recently underscored by the publication of updated ACC/AHA guidelines for measuring blood pressure in patients. However, the recommended position of seating with arms and back supported is not always feasible to achieve clinically, especially for inpatient women who are pregnant. Therefore, it is clinically important to understand the effects of alternative patient positioning on blood pressure measurements. We conducted a review of studies which considered patient position on the effect of blood pressure in pregnancy. This review demonstrates that clinically significant differences may occur based on patient positioning. Despite the small number of primary studies that include pregnant women, notable reductions in blood pressure measurements have been observed in the left lateral recumbent position, a common position during labor or during monitoring, in comparison to measurements taken in the supported seated position. Ultimately, these differences could affect the clinical management of patients and care should be taken to document and consider the position in which the reading was taken.
Keywords: Blood pressure measurement; Fowler's; Left lateral; Patient positioning; Pregnancy; Supine.
Copyright © 2022 International Society for the Study of Hypertension in Pregnancy. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
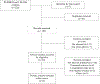
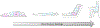
References
-
- Muntner P., Shimbo D., Carey R., Charleston J., Gaillard T., Misra S., Myers MG., Ogedegbe G., Schwartz J., Townsend R., Urbina E., Viera A., White W., Wright J., Measurement of Blood Pressure in Humans: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Hypertension, 2019. 73(5): p. e35–e66. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ngene NC and Moodley J, Physiology of Blood Pressure Relevant to Managing Hypertension in Pregnancy. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med, 2019. 32(8): 1368–77. - PubMed
-
- Nathan H, de Greeff A, Hezelgrave N, Chappell L, Shennan A, Accuracy Validation of the Microlife 3AS1–2 Blood Pressure Device in a Pregnant Population with Low Blood Pressure. Blood Press Monit, 2015. 20(5): 299–302 - PubMed
-
- Nzelu D, Yeung F, Couderq D, Shennan A, and Kametas NA, An Inaccurate Automated Device Negatively Impacts the Diagnosis and Treatment of Gestational Hypertension. Pregnancy Hypertens, 2017. 10: 28–33. - PubMed
-
- Cicolini G, Gagliardi G, and Ballone E, Effect of Fowler’s body position on blood pressure measurement. Journal of Clinical Nursing, 2010. 19:3581–3 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

