Functional signaling test identifies HER2 negative breast cancer patients who may benefit from c-Met and pan-HER combination therapy
- PMID: 34998412
- PMCID: PMC8742957
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-021-00798-9
Functional signaling test identifies HER2 negative breast cancer patients who may benefit from c-Met and pan-HER combination therapy
Abstract
Background: Research is revealing the complex coordination between cell signaling systems as they adapt to genetic and epigenetic changes. Tools to uncover these highly complex functional linkages will play an important role in advancing more efficacious disease treatments. Current tumor cell signal transduction research is identifying coordination between receptor types, receptor families, and transduction pathways to maintain tumor cell viability despite challenging tumor microenvironment conditions.
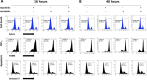
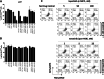
Methods: In this report, coactivated abnormal levels of signaling activity for c-Met and HER family receptors in live tumor cells were measured by a new clinical test to identify a subpopulation of breast cancer patients that could be responsive to combined targeted therapies. The CELsignia Multi-Pathway Signaling Function (CELsignia) Test uses an impedance biosensor to quantify an individual patient's ex vivo live tumor cell signaling response in real-time to specific HER family and c-Met co-stimulation and targeted therapies.
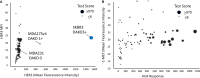
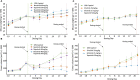
Results: The test identified breast tumors with hyperactive HER1, HER2, HER3/4, and c-Met coordinated signaling that express otherwise normal amounts of these receptors. The supporting data of the pre-clinical verification of this test included analyses of 79 breast cancer patients' cell response to HER and c-Met agonists. The signaling results were confirmed using clinically approved matching targeted drugs, and combinations of targeted drugs in addition to correlative mouse xenograft tumor response to HER and c-Met targeted therapies.
Conclusions: The results of this study demonstrated the potential benefit of a functional test for identifying a subpopulation of breast cancer patients with coordinated abnormal HER and c-Met signaling for a clinical trial testing combination targeted therapy. Video Abstract.
Keywords: Combination targeted therapy; Dysfunctional signaling; HER; c-Met.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors are employed by Celcuity, Inc. 16305 36th Ave N, Suite 100, Minneapolis, MN 55446.
Figures




Similar articles
-
New HER2-negative breast cancer subtype responsive to anti-HER2 therapy identified.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2020 Mar;146(3):605-619. doi: 10.1007/s00432-020-03144-7. Epub 2020 Feb 8. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32036454 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic effects of foretinib with HER-targeted agents in MET and HER1- or HER2-coactivated tumor cells.Mol Cancer Ther. 2011 Mar;10(3):518-30. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-10-0698. Epub 2011 Jan 20. Mol Cancer Ther. 2011. PMID: 21252284
-
Development of a test that measures real-time HER2 signaling function in live breast cancer cell lines and primary cells.BMC Cancer. 2017 Mar 16;17(1):199. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3181-0. BMC Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28302091 Free PMC article.
-
Blockade of the HER family of receptors in the treatment of HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer.Clin Breast Cancer. 2012 Feb;12(1):19-29. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2011.07.001. Epub 2011 Sep 8. Clin Breast Cancer. 2012. PMID: 21903480 Review.
-
Targeting HER family in HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer: potential biomarkers and novel targeted therapies.Pharmacogenomics. 2015;16(3):257-71. doi: 10.2217/pgs.14.133. Pharmacogenomics. 2015. PMID: 25712189 Review.
Cited by
-
The Preclinical Pharmacology of Tepotinib-A Highly Selective MET Inhibitor with Activity in Tumors Harboring MET Alterations.Mol Cancer Ther. 2023 Jul 5;22(7):833-843. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-22-0537. Mol Cancer Ther. 2023. PMID: 36999986 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting c-Met in breast cancer: From mechanisms of chemoresistance to novel therapeutic strategies.Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2024 Oct 22;7:100204. doi: 10.1016/j.crphar.2024.100204. eCollection 2024. Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2024. PMID: 39524211 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Liu X, Wang Q, Yang G, Marando C, Koblish HK, Hall LM, et al. A novel kinase inhibitor, INCB28060, blocks c-MET-dependent signaling, neoplastic activities, and cross-talk with EGFR and HER-3. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17(22):7127–7138. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

