Ceramide signaling in the gut
- PMID: 34998898
- PMCID: PMC8828712
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mce.2022.111554
Ceramide signaling in the gut
Abstract
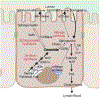
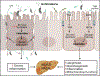
Sphingolipids are essential lipid components in the intestinal epithelial cells (IEC) along the intestinal tract. They play crucial roles in maintaining barrier integrity, regulating nutrient absorption, and acting as signaling molecules to regulate regeneration and differentiation of intestinal mucosa (Kurek et al., 2012). Ceramide is the central sphingolipid species and the precursor of all complex sphingolipids and other downstream simple intermediates like sphingosine (SPH), ceramide-1-phosphate (C-1-P), and sphingosine-1-phosphate (S-1-P). It is also a critical signaling molecule regulating numerous physiologic and pathologic processes. This review will summarize the metabolism of ceramides in the gut and their regulation in inflammatory bowel diseases and colorectal cancer.
Keywords: Ceramide; Colon cancer; Inflammatory bowel disease; Intestine; NAFLD.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest
SAS is a founder and shareholder with Centaurus Therapeutics.
Figures
References
-
- Kurek K, Piotrowska DM, Wiesiolek P, Chabowski A, and Zendzian-Piotrowska M, [Role of sphingolipids in digestive system]. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online) 66 (2012) 868–75. - PubMed
-
- Duan RD, and Nilsson A, Metabolism of sphingolipids in the gut and its relation to inflammation and cancer development. Prog Lipid Res 48 (2009) 62–72. - PubMed
-
- Merrill AH Jr., De novo sphingolipid biosynthesis: a necessary, but dangerous, pathway. J Biol Chem 277 (2002) 25843–6. - PubMed
-
- Futerman AH, and Riezman H, The ins and outs of sphingolipid synthesis. Trends Cell Biol 15 (2005) 312–8. - PubMed
-
- Park JW, Park WJ, and Futerman AH, Ceramide synthases as potential targets for therapeutic intervention in human diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta 1841 (2014) 671–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

