Gene therapy with Pellino-1 improves perfusion and decreases tissue loss in Flk-1 heterozygous mice but fails in MAPKAP Kinase-2 knockout murine hind limb ischemia model
- PMID: 34999110
- PMCID: PMC9250804
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mvr.2022.104311
Gene therapy with Pellino-1 improves perfusion and decreases tissue loss in Flk-1 heterozygous mice but fails in MAPKAP Kinase-2 knockout murine hind limb ischemia model
Abstract
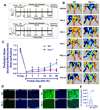
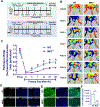
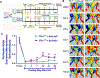
Objectives: In the United States, over 8.5 million people suffer from peripheral arterial disease (PAD). Previously we reported that Pellino-1(Peli1) gene therapy reduces ischemic damage in the myocardium and skin flaps in Flk-1 [Fetal Liver kinase receptor-1 (Flk-1)/ Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2/VEGFR2] heterozygous (Flk-1+/--) mice. The present study compares the angiogenic response and perfusion efficiency following hind limb ischemia (HLI) in, Flk-1+/- and, MAPKAPKINASE2 (MK2-/-) knockout (KO) mice to their control wild type (WT). We also demonstrated the use of Peli1 gene therapy to improve loss of function following HLI.
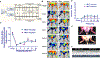
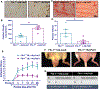
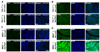
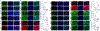
Study design and methods: Femoral artery ligation (HLI) was performed in both Flk-1+/- and MK2-/- mice along with their corresponding WT. Another set of Flk-1+/- and MK2-/- were injected with either Adeno-LacZ (Ad.LacZ) or Adeno-Peli1 (Ad.Peli1) after HLI. Hind limb perfusion was assessed by laser doppler imaging at specific time points. A standardized scoring scale is used to quantify the extent of ischemia. Histology analysis performed includes capillary density, fibrosis, pro-angiogenic and anti-apoptotic proteins.
Results: Flk-1+/- and MK2-/- had a slower recovery of perfusion efficiency in the ischemic limbs than controls. Both Flk-1+/- and MK2-/- KO mice showed decreased capillary density and capillary myocyte ratios with increased fibrosis than their corresponding wild types. Ad.Peli1 injected ischemic Flk-1+/- limb showed improved perfusion, increased capillary density, and pro-angiogenic molecules with reduced fibrosis compared to Ad.LacZ group. No significant improvement in perfusion was observed in MK2-/- ischemic limb after Ad. Peli1 injection.
Conclusion: Deletion of Flk-1 and MK2 impairs neovascularization and perfusion following HLI. Treatment with Ad. Peli1 results in increased angiogenesis and improved perfusion in Flk-1+/- mice but fails to rectify perfusion in MK2 KO mice. Overall, Peli1 gene therapy is a promising candidate for the treatment of PAD.
Keywords: Hind limb ischemia; Ischemic score; Peli1; Perfusion; VEGF signaling.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
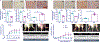

Similar articles
-
Disruption of VEGF Mediated Flk-1 Signaling Leads to a Gradual Loss of Vessel Health and Cardiac Function During Myocardial Infarction: Potential Therapy With Pellino-1.J Am Heart Assoc. 2018 Sep 18;7(18):e007601. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.117.007601. J Am Heart Assoc. 2018. PMID: 30371196 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of newly described pro-survival molecule Pellino-1 increases oxidative stress, downregulates cIAP2/NF-κB cell survival pathway, reduces angiogenic response, and thereby aggravates tissue function in mouse ischemic models.Basic Res Cardiol. 2020 Jun 14;115(4):45. doi: 10.1007/s00395-020-0804-4. Basic Res Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 32537701
-
Overexpression of Thioredoxin1 enhances functional recovery in a mouse model of hind limb ischemia.J Surg Res. 2017 Aug;216:158-168. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2017.04.019. Epub 2017 May 5. J Surg Res. 2017. PMID: 28807201
-
A Murine Model of Hind Limb Ischemia to Study Angiogenesis and Arteriogenesis.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1717:135-143. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7526-6_11. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29468589 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Redox regulation of ischemic limb neovascularization - What we have learned from animal studies.Redox Biol. 2017 Aug;12:1011-1019. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2017.04.040. Epub 2017 May 4. Redox Biol. 2017. PMID: 28505880 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
IGF-1 Therapy Improves Muscle Size and Function in Experimental Peripheral Arterial Disease.JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2023 Mar 8;8(6):702-719. doi: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2022.12.006. eCollection 2023 Jun. JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2023. PMID: 37426532 Free PMC article.
-
E3 Ubiquitin Ligases in Endothelial Dysfunction and Vascular Diseases: Roles and Potential Therapies.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2023 Aug 1;82(2):93-103. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000001441. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37314134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biology of Pellino1: a potential therapeutic target for inflammation in diseases and cancers.Front Immunol. 2023 Dec 18;14:1292022. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1292022. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38179042 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Asahara T, et al., 1998. Tie2 receptor ligands, angiopoietin-1 and angiopoietin-2, modulate VEGF-induced postnatal neovascularization. Circ Res. 83, 233–40. - PubMed
-
- Banai S, et al., 1994. Angiogenic-induced enhancement of collateral blood flow to ischemic myocardium by vascular endothelial growth factor in dogs. Circulation. 89, 2183–9. - PubMed
-
- Belch J, et al., 2011. Effect of fibroblast growth factor NV1FGF on amputation and death: a randomised placebo-controlled trial of gene therapy in critical limb ischaemia. Lancet. 377, 1929–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

