Characterization of cognitive impairment in adult polyglucosan body disease
- PMID: 34999962
- PMCID: PMC9119871
- DOI: 10.1007/s00415-022-10960-z
Characterization of cognitive impairment in adult polyglucosan body disease
Abstract
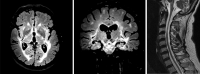
Adult polyglucosan body disease (APBD) is a rare but probably underdiagnosed autosomal recessive neurodegenerative disorder due to pathogenic variants in GBE1. The phenotype is characterized by neurogenic bladder dysfunction, spastic paraplegia, and axonal neuropathy. Additionally, cognitive symptoms and dementia have been reported in APBD but have not been studied systematically. Using exome sequencing, we identified two previously unreported bi-allelic missense GBE1 variants in a patient with severe memory impairment along with the typical non-cognitive symptoms. We were able to confirm a reduction of GBE1 activity in blood lymphocytes. To characterize the neuropsychological profile of patients suffering from APBD, we conducted a systematic review of cognitive impairment in this rare disease. Analysis of 24 cases and case series (in total 58 patients) showed that executive deficits and memory impairment are the most common cognitive symptoms in APBD.
Keywords: Adult polyglucosan body disease; Cognitive impairment; Dementia; GBE1; Glycogen-branching enzyme.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in regard to this work.
Figures


References
-
- Farmer JG, Crain BJ, Harris BT, Turner RS. Coexisting adult polyglucosan body disease with frontotemporal lobar degeneration with transactivation response DNA-binding protein-43 (TDP-43)-positive neuronal inclusions. Neurocase. 2013;19(1):67–75. doi: 10.1080/13554794.2011.654217. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

