Structures and biological functions of zinc finger proteins and their roles in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 35000617
- PMCID: PMC8744215
- DOI: 10.1186/s40364-021-00345-1
Structures and biological functions of zinc finger proteins and their roles in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
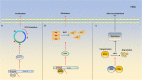
Zinc finger proteins are transcription factors with the finger domain, which plays a significant role in gene regulation. As the largest family of transcription factors in the human genome, zinc finger (ZNF) proteins are characterized by their different DNA binding motifs, such as C2H2 and Gag knuckle. Different kinds of zinc finger motifs exhibit a wide variety of biological functions. Zinc finger proteins have been reported in various diseases, especially in several cancers. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the third leading cause of cancer-associated death worldwide, especially in China. Most of HCC patients have suffered from hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) injection for a long time. Although the surgical operation of HCC has been extremely developed, the prognosis of HCC is still very poor, and the underlying mechanisms in HCC tumorigenesis are still not completely understood. Here, we summarize multiple functions and recent research of zinc finger proteins in HCC tumorigenesis and progression. We also discuss the significance of zinc finger proteins in HCC diagnosis and prognostic evaluation.
Keywords: Biological function; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Transcription factor; Transcription regulation; Zinc finger protein.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

