Singapore Neonatal Resuscitation Guidelines 2021
- PMID: 35001116
- PMCID: PMC8804489
- DOI: 10.11622/smedj.2021110
Singapore Neonatal Resuscitation Guidelines 2021
Abstract
Neonatal resuscitation is a coordinated, team-based series of timed sequential steps that focuses on a transitional physiology to improve perinatal and neonatal outcomes. The practice of neonatal resuscitation has evolved over time and continues to be shaped by emerging evidence as well as key opinions. We present the revised Neonatal Resuscitation Guidelines for Singapore 2021. The recommendations from the International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation Neonatal Task Force Consensus on Science and Treatment Recommendations (2020) and guidelines from the American Heart Association and European Resuscitation Council were compared with existing guidelines. The recommendations of the Neonatal Subgroup of the Singapore Resuscitation and First Aid Council were derived after the work group discussed and appraised the current available evidence and their applicability to local clinical practice.
Keywords: Singapore Resuscitation and First Aid Council (SRFAC) guidelines for resuscitation 2021; neonatal resuscitation; newborn resuscitation.
Copyright: © Singapore Medical Association.
Figures
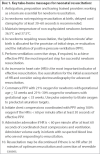
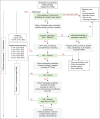

References
-
- Ersdal HL, Linde J, Mduma E, Auestad B, Perlman J. Neonatal outcome following cord clamping after onset of spontaneous respiration. Pediatrics. 2014;134:265–72. - PubMed
-
- Niles DE, Cines C, Insley E, et al. Incidence and characteristics of positive pressure ventilation delivered to newborns in a US tertiary academic hospital. Resuscitation. 2017;115:102–9. - PubMed
-
- Perlman JM, Risser R. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation in the delivery room. Associated clinical events. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 1995;149:20–5. - PubMed
-
- Halling C, Sparks JE, Christie L, Wyckoff MH. Efficacy of intravenous and endotracheal epinephrine during neonatal cardiopulmonary resuscitation in the delivery room. J Pediatr. 2017;185:232–6. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

