Dissipative Particle Dynamics Simulation of Ultrasound Propagation through Liquid Water
- PMID: 35001631
- PMCID: PMC8830050
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jctc.1c01020
Dissipative Particle Dynamics Simulation of Ultrasound Propagation through Liquid Water
Abstract
Ultrasound is widely used as a noninvasive method in therapeutic and diagnostic applications. These can be further optimized by computational approaches, as they allow for controlled testing and rational optimization of the ultrasound parameters, such as frequency and amplitude. Usually, continuum numerical methods are used to simulate ultrasound propagating through different tissue types. In contrast, ultrasound simulations using particle description are less common, as the implementation is challenging. In this work, a dissipative particle dynamics model is used to perform ultrasound simulations in liquid water. The effects of frequency and thermostat parameters are studied and discussed. We show that frequency and thermostat parameters affect not only the attenuation but also the computed speed of sound. The present study paves the way for development and optimization of a virtual ultrasound machine for large-scale biomolecular simulations.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


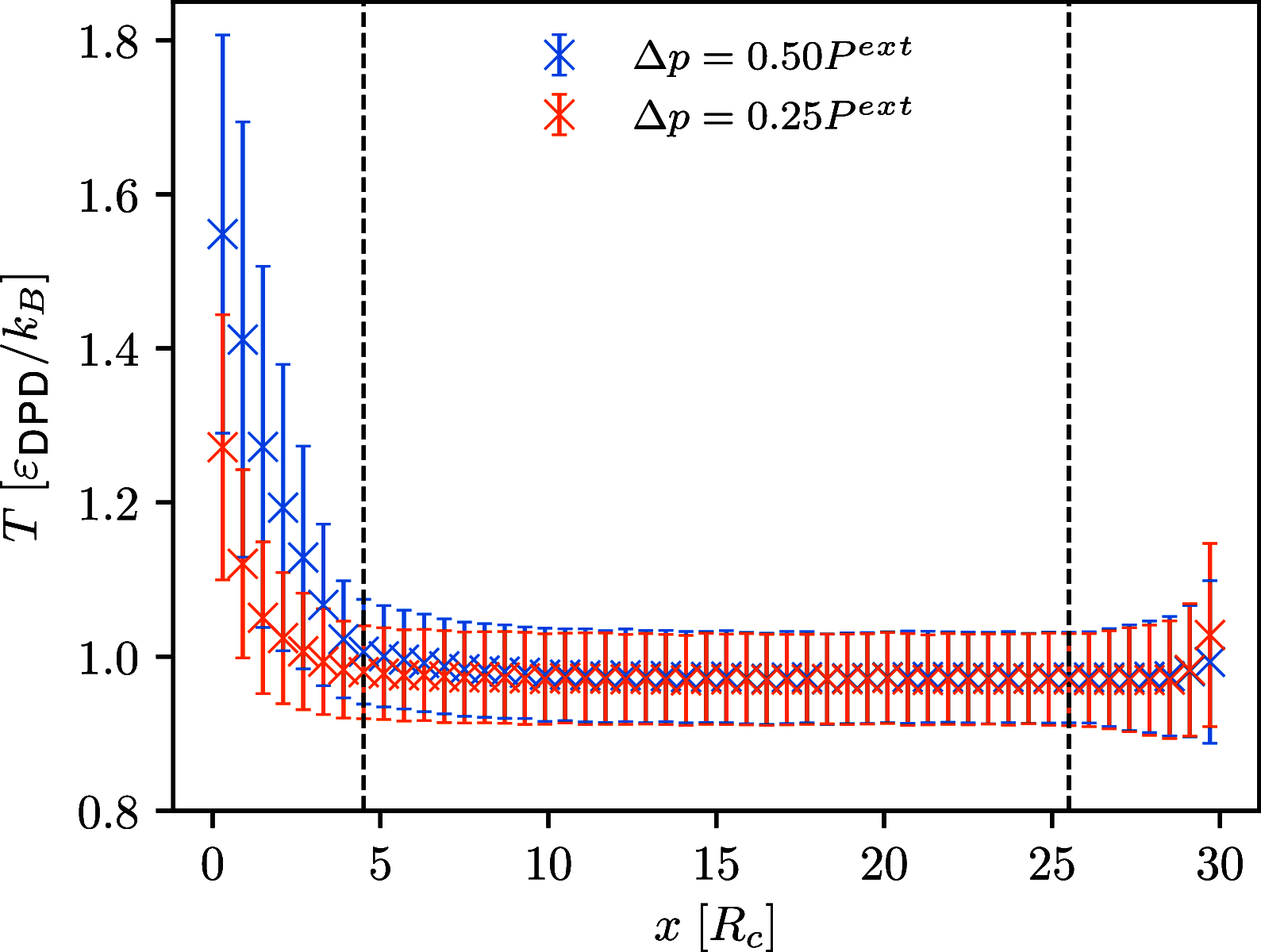
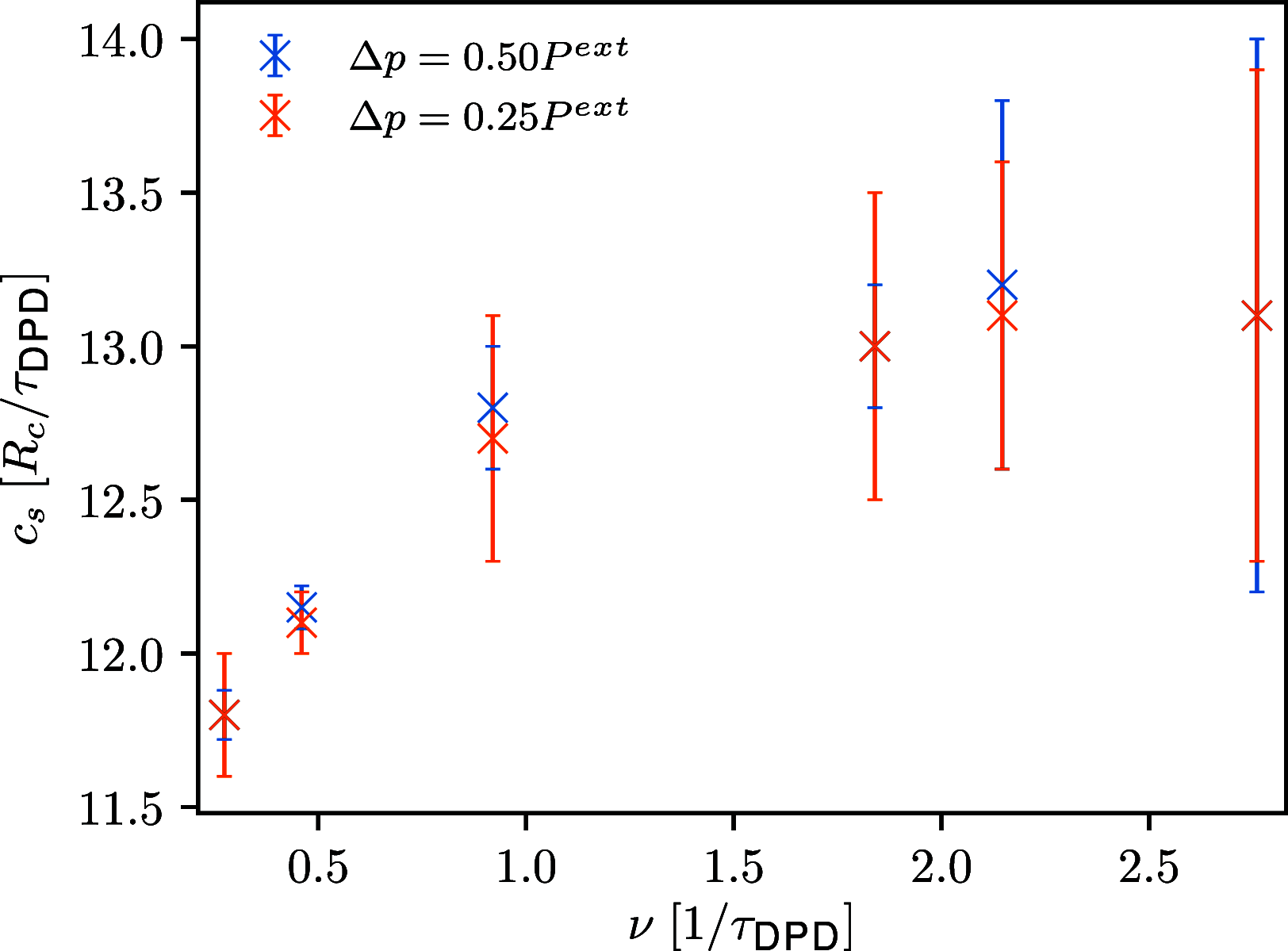





Similar articles
-
Open-boundary molecular dynamics of ultrasound using supramolecular water models.J Chem Phys. 2025 Jan 14;162(2):024103. doi: 10.1063/5.0238348. J Chem Phys. 2025. PMID: 39774894
-
Transport properties controlled by a thermostat: An extended dissipative particle dynamics thermostat.Soft Matter. 2007 Dec 11;4(1):156-161. doi: 10.1039/b713568h. Soft Matter. 2007. PMID: 32907095
-
Micro-scale finite element modeling of ultrasound propagation in aluminum trabecular bone-mimicking phantoms: A comparison between numerical simulation and experimental results.Ultrasonics. 2016 May;68:17-28. doi: 10.1016/j.ultras.2016.01.014. Epub 2016 Feb 4. Ultrasonics. 2016. PMID: 26894840
-
Exploring membrane and protein dynamics with dissipative particle dynamics.Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2011;85:143-82. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-386485-7.00004-1. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2011. PMID: 21920323 Review.
-
Droplets, Bubbles and Ultrasound Interactions.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;880:157-74. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-22536-4_9. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 26486337 Review.
Cited by
-
Dissipative Particle Dynamics Models of Encapsulated Microbubbles and Nanoscale Gas Vesicles for Biomedical Ultrasound Simulations.ACS Appl Nano Mater. 2025 Aug 4;8(32):16053-16070. doi: 10.1021/acsanm.5c02783. eCollection 2025 Aug 15. ACS Appl Nano Mater. 2025. PMID: 40837281 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Udroiu I. Ultrasonic drug delivery in Oncology. JBUON 2015, 20, 381–390. - PubMed
-
- Sofferman R. A. In Ultrasound of the Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands; Sofferman R. A., Ahuja A. T., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, 2012; pp 9–19.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

