Linear IGA bullous dermatosis potentially triggered by vaccination
- PMID: 35001680
- PMCID: PMC8753231
- DOI: 10.1177/20587384211021218
Linear IGA bullous dermatosis potentially triggered by vaccination
Abstract
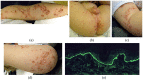
Linear IgA bullous dermatosis (LABD) is a mucocutaneous autoimmune blistering disease affecting both adults and children. It is caused by IgA antibodies targeting multiple antigens along the basement membrane zone, leading to disruption of dermoepidermal junction and development of bullous lesions which often presents in characteristic arrangement. Although most LABD cases have been reported to be idiopathic, different triggers have been described, including several drugs and infection. However, the occurrence of vaccine-induced cases of LABD is not widely known and accepted due to the few reports available. We present two cases of LABD occurred following different triggers, rising the suspicion for a possible pathogenetic role of vaccines.
Keywords: adverse reaction; autoimmune blistering disease; dermatology; linear IgA bullous dermatosis; papillomavirus; vaccines.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Fortuna G, Marinkovich MP. (2012) Linear immunoglobulin A bullous dermatosis. Clinics in Dermatology 30(1): 38–50. - PubMed
-
- Kartan S, Shi VY, Clark AK, et al. (2017) Paraneoplastic pemphigus and autoimmune blistering diseases associated with neoplasm: Characteristics, diagnosis, associated neoplasms, proposed pathogenesis, treatment. American Journal of Clinical Dermatology 18(1): 105–126. - PubMed
-
- Alberta-Wszolek L, Mousette AM, Mahalingam M, et al. (2009) Linear IgA bullous dermatosis following influenza vaccination. Dermatology Online Journal 15(11): 3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

