Quantitative analysis of efficacy and safety of LABA/LAMA fixed-dose combinations in the treatment of stable COPD
- PMID: 35001708
- PMCID: PMC8743917
- DOI: 10.1177/17534666211066068
Quantitative analysis of efficacy and safety of LABA/LAMA fixed-dose combinations in the treatment of stable COPD
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to quantitatively compare the efficacy and safety of long-acting β2-agonist (LABA)/long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA) fixed-dose combinations (FDCs) for the treatment of stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), especially in terms of their loss of efficacy in lung function.
Methods: Randomized controlled clinical trials of LABA/LAMA FDCs for the treatment of stable COPD were comprehensively searched for in public databases. Pharmacodynamic models were established to describe the time course of the primary outcome [trough forced expiratory volume in the first second (FEV1)]. Secondary outcomes [COPD exacerbations, St. George's Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ), Transition Dyspnoea Index (TDI), and rescue medication use] and safety outcomes [mortality, serious adverse events (SAEs), and withdrawals due to adverse events (AEs)] were also compared via a meta-analysis.
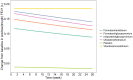
Results: A total of 22 studies involving 16,486 participants were included in this study. The results showed that in terms of primary outcome (change from baseline in trough FEV1), the efficacy of vilanterol/umeclidinium was the highest, while the efficacy of formoterol/aclidinium was the lowest, with a maximum effect value (Emax) of 0.185 L [95% confidence interval (CI): 0.173-0.197 L] and 0.119 L (95% CI: 0.103-0.135 L), respectively. The efficacy of other drugs, such as formoterol/glycopyrronium, indacaterol/glycopyrronium, and olodaterol/tiotropium, were comparable, and their Emax values were 0.150-0.177 L. Except for vilanterol/umeclidinium, the other four LABA/LAMA FDCs showed a certain degree of loss of efficacy. Compared with the efficacy at 2 days, the trough FEV1 (L) relative to baseline at 24 weeks decreased by 0.029-0.041 L. In terms of secondary outcomes, the efficacy of different LABA/LAMA FDCs was similar in TDI and rescue medication use. However, formoterol/aclidinium was better in preventing the COPD exacerbations, while vilanterol/umeclidinium was the best in terms of SGRQ. In addition, different LABA/LAMA FDCs and placebo had similar safety outcomes.
Conclusion: The present findings may provide necessary quantitative information for COPD medication guidelines.
Keywords: LABA/LAMA fixed-dose combinations; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; model-based meta-analysis; trough forced expiratory volume in 1 second.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Impact of ICS/LABA and LABA/LAMA FDCs on functional and clinical outcomes in COPD: A network meta-analysis.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2019 Dec;59:101855. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2019.101855. Epub 2019 Oct 19. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2019. PMID: 31639476
-
Systematic review and network meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of glycopyrrolate/formoterol fumarate metered dose inhaler in comparison with other long-acting muscarinic antagonist/long-acting β2-agonist fixed-dose combinations in COPD.Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2019 Jan-Dec;13:1753466619894502. doi: 10.1177/1753466619894502. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2019. PMID: 31868101 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Budesonide/Glycopyrronium/Formoterol Fumarate Metered Dose Inhaler (BGF MDI) Versus Other Inhaled Corticosteroid/Long-Acting Muscarinic Antagonist/Long-Acting β2-Agonist (ICS/LAMA/LABA) Triple Combinations in COPD: A Systematic Literature Review and Network Meta-analysis.Adv Ther. 2020 Jun;37(6):2956-2975. doi: 10.1007/s12325-020-01311-3. Epub 2020 Apr 25. Adv Ther. 2020. PMID: 32335859 Free PMC article.
-
Combined aclidinium bromide and long-acting beta2-agonist for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Dec 11;12(12):CD011594. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011594.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30536566 Free PMC article.
-
LABA/LAMA versus LABA/ICS fixed-dose combinations in the prevention of COPD exacerbations: a modeling analysis of literature aggregate data.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2023 Oct;79(10):1321-1332. doi: 10.1007/s00228-023-03543-y. Epub 2023 Jul 29. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37507595
Cited by
-
Systemic Manifestations of COPD and the Impact of Dual Bronchodilation with Tiotropium/Olodaterol on Cardiac Function and Autonomic Integrity.J Clin Med. 2024 May 16;13(10):2937. doi: 10.3390/jcm13102937. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38792478 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of humidified high-flow nasal cannula oxygen therapy on respiratory function recovery in stable COPD patients.Am J Transl Res. 2022 Jun 15;14(6):4074-4081. eCollection 2022. Am J Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 35836894 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment patterns in patients with stable COPD in China: analysis of a prospective, 52-week, nationwide, observational cohort study (REAL).Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2023 Jan-Dec;17:17534666231158283. doi: 10.1177/17534666231158283. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2023. PMID: 37013442 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lopez AD, Shibuya K, Rao C, et al. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: current burden and future projections. Eur Respir J 2006; 27(2): 397–412. - PubMed
-
- Celli BR. Pharmacological therapy of COPD: reasons for optimism. Chest 2018; 154(6): 1404–1415. - PubMed
-
- Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease 2021 report, 2020, https://goldcopd.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/GOLD-REPORT-2021-v1.1-25... (accessed 17 November 2020). - PubMed
-
- Calzetta L, Rogliani P, Matera MG, et al. A Systematic review with meta-analysis of dual bronchodilation with LAMA/LABA for the treatment of stable COPD. Chest 2016; 149(5): 1181–1196. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

