Yi Shen An, a Chinese traditional prescription, ameliorates membranous glomerulonephritis induced by cationic bovine serum albumin in rats
- PMID: 35001799
- PMCID: PMC8745358
- DOI: 10.1080/13880209.2021.2021947
Yi Shen An, a Chinese traditional prescription, ameliorates membranous glomerulonephritis induced by cationic bovine serum albumin in rats
Abstract
Context: Yi Shen An (YSA) is an investigational composite of traditional Chinese medicine (Reference: 2010L000974) for the treatment of renal disease.
Objective: To investigate the protective effects of YSA against membranous glomerulonephritis (MGN).
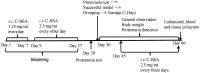
Materials and methods: Male Sprague-Dawley rats were injected with cationic bovine serum albumin (C-BSA) to create a model of MGN. Then, rats were orally treated with YSA at doses of 0.25, 0.5, 1 and 2 g/kg for 35 successive days; prednisone (5 mg/kg) was used as a positive control. At the end of the experimental period, we performed a series of tests, including 24 h urinary protein, and biochemical, immunological, antioxidative, coagulation indices, and histopathological examination.
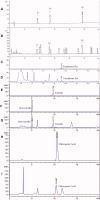
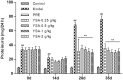
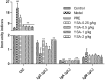
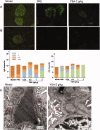
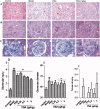
Results: YSA-1 g/kg significantly lowered urinary protein from 68.37 to 30.74 mg (p < 0.01). Meantime, total protein (TP) and albumin (ALB) recovered from 66.26 and 20.51 g/L to 76.08 and 35.64 g/L (p < 0.01), respectively. YSA removed the deposition of immunoglobulin G (IgG) and complement 3c (C3c), prevented inter-capillary cell hyperplasia on the glomerular basement membrane (GBM), and reduced electron-dense deposits and fusion of podocytes. In addition, serum IgG and superoxide dismutase were significantly elevated. In contrast, malondialdehyde, total cholesterol, triglyceride, circulating immune complex (CIC), and immunoglobulin M decreased in the YSA-treated group. Moreover, the blood coagulation dysfunction was adjusted.
Discussion and conclusions: These findings indicate YSA may exert a therapeutic effect against MGN through the inhibition of CIC formation, and the removal of IgG and C3c deposition from the GBM, thus supporting the development of further clinical trials.
Keywords: Nephritis; circulating immune complex; podocytes; proteinuria.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Diosgenin protects against cationic bovine serum albumin-induced membranous glomerulonephritis by attenuating oxidative stress and renal inflammation via the NF-κB pathway.Pharm Biol. 2024 Dec;62(1):285-295. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2024.2330602. Epub 2024 Mar 22. Pharm Biol. 2024. PMID: 38516898 Free PMC article.
-
Renoprotective Effects Of Isoliquiritin Against Cationic Bovine Serum Albumin-Induced Membranous Glomerulonephritis In Experimental Rat Model Through Its Anti-Oxidative And Anti-Inflammatory Properties.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019 Oct 30;13:3735-3751. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S213088. eCollection 2019. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019. PMID: 31802848 Free PMC article.
-
Zhen-wu-tang attenuates cationic bovine serum albumin-induced inflammatory response in membranous glomerulonephritis rat through inhibiting AGEs/RAGE/NF-κB pathway activation.Int Immunopharmacol. 2016 Apr;33:33-41. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2016.01.008. Epub 2016 Feb 4. Int Immunopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26851631
-
A patent herbal drug Yi-Shen-Hua-Shi granule ameliorates C-BSA-induced chronic glomerulonephritis and inhabits TGFβ signaling in rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2019 May 23;236:258-262. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.02.044. Epub 2019 Mar 2. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30836175
-
Advances in membranous nephropathy: success stories of a long journey.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2011 Jul;38(7):460-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2011.05506.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21388432 Review.
Cited by
-
Barleriside A, an aryl hydrocarbon receptor antagonist, ameliorates podocyte injury through inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammation.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Aug 22;15:1386604. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1386604. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39239643 Free PMC article.
-
Diosgenin protects against cationic bovine serum albumin-induced membranous glomerulonephritis by attenuating oxidative stress and renal inflammation via the NF-κB pathway.Pharm Biol. 2024 Dec;62(1):285-295. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2024.2330602. Epub 2024 Mar 22. Pharm Biol. 2024. PMID: 38516898 Free PMC article.
-
Safranal Ameliorates Renal Damage, Inflammation, and Podocyte Injury in Membranous Nephropathy via SIRT/NF-κB Signalling.Curr Med Sci. 2025 Apr;45(2):288-300. doi: 10.1007/s11596-025-00020-8. Epub 2025 Mar 4. Curr Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40035996 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Austin HA, Muenz LR, Joyce KM, Antonovych TT, Balow JE.. 1984. Diffuse proliferative lupus nephritis: identification of specific pathologic features affecting renal outcome. Kidney Int. 25(4):689–695. - PubMed
-
- Bao LP, Li JS, Zhang DQ, Zhang L, Gao P, Yao T, Wu XY.. 2018. Chlorogenic acid prevents diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammation through modulation of the Nrf2/HO-1 and NF-ĸB pathways. Int Immunopharmacol. 54:245–253. - PubMed
-
- Barbour SJ, Greenwald A, Djurdjev O, Levin A, Hladunewich MA, Nachman PH, Hogan SL, Cattran DC, Reich HN.. 2012. Disease-specific risk of venous thromboembolic events is increased in idiopathic glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 81(2):190–195. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
