Comparison of effects of dexmedetomidine added to ropivacaine versus ropivacaine alone infiltration scalp block for attenuation of the haemodynamic response to skull pin placement in neurosurgical procedures: A double-blind, randomised clinical trial
- PMID: 35001949
- PMCID: PMC8680418
- DOI: 10.4103/ija.ija_450_21
Comparison of effects of dexmedetomidine added to ropivacaine versus ropivacaine alone infiltration scalp block for attenuation of the haemodynamic response to skull pin placement in neurosurgical procedures: A double-blind, randomised clinical trial
Abstract
Background and aims: Skull pin head holder application is intensely painful and is accompanied with abrupt increase in heart rate and arterial blood pressure. We aimed to determine the effects of adding dexmedetomidine to ropivacaine scalp block in attenuating the haemodynamic response to skull pin insertion in neurosurgical procedures.
Methods: Sixty patients were randomly allocated to receive scalp block with 25 ml of 0.5% ropivacaine added with either normal saline (control group) or dexmedetomidine (1 μg/kg) after anesthesia induction. A standard uniform general endotracheal anaesthesia protocol was followed in all study subjects. Heart rate and blood pressure measurements were made at baseline, 1, 3, 5, 10, and 15 min following skull pin placement. Student's independent t-test, Chi-square test and repeated measure analysis of variance were used to analyse the obtained data.
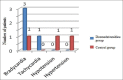
Results: There was no significant attenuation of heart rate (P = 0.418), systolic (P = 0.542), diastolic (P = 0.793) and mean blood pressure (P = 0.478) with addition of dexmedetomidine to ropivacaine.
Conclusions: The addition of dexmedetomidine (1 μg/kg) to 25 ml of 0.5% ropivacaine offers no additional benefit over 25 ml of 0.5% ropivacaine alone scalp block in attenuating the haemodynamic response to skull pin placement in neurosurgical procedures.
Keywords: Blood pressure; dexmedetomidine; heart rate; nerve block; ropivacaine.
Copyright: © 2021 Indian Journal of Anaesthesia.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison between intravenous dexmedetomidine and local lignocaine infiltration to attenuate the haemodynamic response to skull pin head holder application during craniotomy.Indian J Anaesth. 2015 Dec;59(12):785-8. doi: 10.4103/0019-5049.171558. Indian J Anaesth. 2015. PMID: 26903671 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of dexmedetomidine and fentanyl to prevent haemodynamic response to skull pin application in neurosurgery: double blind randomized controlled trial.Anaesthesiol Intensive Ther. 2017;49(4):268-273. doi: 10.5603/AIT.a2017.0051. Epub 2017 Oct 13. Anaesthesiol Intensive Ther. 2017. PMID: 29027653 Clinical Trial.
-
Evaluation of the Hemodynamic Response of Intravenous Clonidine versus Ropivacaine Scalp Block to Insertion of Scalp Pins in Neurosurgical Patients.Anesth Essays Res. 2018 Jan-Mar;12(1):213-217. doi: 10.4103/0259-1162.194572. Anesth Essays Res. 2018. PMID: 29628584 Free PMC article.
-
Attenuation of Hemodynamic Response to Skull Pin Head Holder Insertion: Intravenous Clonidine versus Intravenous Lignocaine Infusion.Anesth Essays Res. 2017 Jan-Mar;11(1):129-133. doi: 10.4103/0259-1162.186592. Anesth Essays Res. 2017. PMID: 28298771 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of intravenous dexmedetomidine on hemodynamic response in patients undergoing skull-pin head-holder application during neurosurgery - A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2020 Aug;195:105939. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2020.105939. Epub 2020 May 20. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2020. PMID: 32480196
Cited by
-
Dexmedetomidine: A drug for all seasons?Indian J Anaesth. 2021 Nov;65(11):789-791. doi: 10.4103/ija.ija_964_21. Epub 2021 Nov 23. Indian J Anaesth. 2021. PMID: 35001950 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Efficacy of Adding Clonidine to Bupivacaine 0.25% Versus Plain Bupivacaine 0.25% Infiltration in Scalp Blocks for Supratentorial Craniotomy.Cureus. 2025 Jun 3;17(6):e85274. doi: 10.7759/cureus.85274. eCollection 2025 Jun. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40612854 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the Effect of Scalp Block With Ropivacaine vs. Ropivacaine and Clonidine on Postoperative Pain in Patients Undergoing Craniotomy Surgery Under General Anesthesia.Cureus. 2024 Aug 20;16(8):e67342. doi: 10.7759/cureus.67342. eCollection 2024 Aug. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39310564 Free PMC article.
-
Intravenous dexmedetomidine versus levobupivacaine for hemodynamic response towards skull pin insertion.Bioinformation. 2025 Mar 31;21(3):434-440. doi: 10.6026/973206300210434. eCollection 2025. Bioinformation. 2025. PMID: 40599956 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agarwal A, Sinha PK, Pandey CM. Effect of a subanaesthetic dose of intravenous ketamine and/or local anaesthetic infiltration on hemodynamic responses to skull-pin placement: A prospective, placebo-controlled, randomized, double-blind study. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 2001;13:189–94. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources