Comparison of sensory posterior articular nerves of the knee (SPANK) block versus infiltration between the popliteal artery and the capsule of the knee (IPACK) block when added to adductor canal block for pain control and knee rehabilitation after total knee arthroplasty---A prospective randomised trial
- PMID: 35001951
- PMCID: PMC8680422
- DOI: 10.4103/ija.ija_682_21
Comparison of sensory posterior articular nerves of the knee (SPANK) block versus infiltration between the popliteal artery and the capsule of the knee (IPACK) block when added to adductor canal block for pain control and knee rehabilitation after total knee arthroplasty---A prospective randomised trial
Abstract
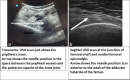
Background and aims: Adductor canal block (ACB), though an effective procedure for postoperative analgesia in total knee arthroplasty (TKA), does not provide analgesia to the posterior articular aspect of the knee joint. Infiltration between the popliteal artery and the capsule of the knee (IPACK block) and sensory posterior articular nerves of the knee (SPANK block) are two single injection techniques that have been shown to provide effective analgesia in posterior knee pain. This study aims to compare the effect of IPACK block and SPANK block when combined with ACB for analgesia and postoperative rehabilitation in TKA.
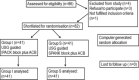
Methods: A total of 82 patients were randomised into two groups: (1) ACB combined with IPACK, (2) ACB combined with SPANK block. The primary outcome was the pain scores from 6 h to 48 h after surgery and the duration of postoperative analgesia. The secondary outcome measures were 24 h opioid consumption, ambulation parameters like mobilisation ability, quadriceps muscle strength and patient satisfaction score at discharge.
Results: Numerical rating scale (NRS) scores at rest and on movement, duration of analgesia, total opioid consumption, and patient satisfaction were significantly better (P < 0.05%) in the IPACK group than in the SPANK block. There were no significant differences in the knee rehabilitation parameters between the blocks.
Conclusion: ACB with IPACK block offers better analgesia, less opioid consumption and better patient satisfaction with comparable knee rehabilitation parameters in the immediate postoperative period after TKA compared to ACB with SPANK block.
Keywords: Analgesia; arthroplasty; knee; nerve block; ultrasonography.
Copyright: © 2021 Indian Journal of Anaesthesia.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Pelt CE, Anderson AW, Anderson MB, Van Dine C, Peters CL. Post-operative falls after total knee arthroplasty in patients with a femoral nerve catheter: Can we reduce the incidence? J Arthroplasty. 2014;29:1154–7. - PubMed
-
- Vora MU, Nicholas TA, Kassel CA, Grant SA. Adductor canal block for knee surgical procedures: Review article. J Clin Anesth. 2016;35:295–303. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical