Forecasting carbon futures price: a hybrid method incorporating fuzzy entropy and extreme learning machine
- PMID: 35002000
- PMCID: PMC8717830
- DOI: 10.1007/s10479-021-04406-4
Forecasting carbon futures price: a hybrid method incorporating fuzzy entropy and extreme learning machine
Abstract
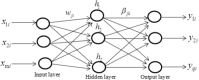
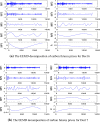
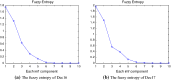
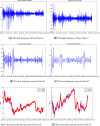
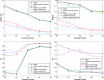
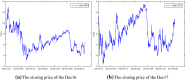
In this paper, we propose a novel hybrid model that extends prior work involving ensemble empirical mode decomposition (EEMD) by using fuzzy entropy and extreme learning machine (ELM) methods. We demonstrate this 3-stage model by applying it to forecast carbon futures prices which are characterized by chaos and complexity. First, we employ the EEMD method to decompose carbon futures prices into a couple of intrinsic mode functions (IMFs) and one residue. Second, the fuzzy entropy and K-means clustering methods are used to reconstruct the IMFs and the residue to obtain three reconstructed components, specifically a high frequency series, a low frequency series, and a trend series. Third, the ARMA model is implemented for the stationary high and low frequency series, while the extreme learning machine (ELM) model is utilized for the non-stationary trend series. Finally, all the component forecasts are aggregated to form final forecasts of the carbon price for each model. The empirical results show that the proposed reconstruction algorithm can bring more than 40% improvement in prediction accuracy compared to the traditional fine-to-coarse reconstruction algorithm under the same forecasting framework. The hybrid forecasting model proposed in this paper also well captures the direction of the price changes, with strong and robust forecasting ability, which is significantly better than the single forecasting models and the other hybrid forecasting models.
Keywords: ARMA; Carbon futures price; EEMD; Extreme learning machine; Fuzzy entropy; K-means clustering method.
© The Author(s) 2021.
Figures


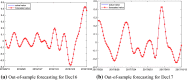
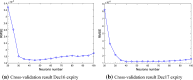

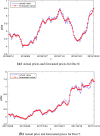
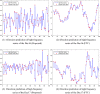

References
-
- Arouri, M. E. H., Jawadi, F., & Nguyen, D. K. (2012). Nonlinearities in carbon spot-futures price relationships during Phase II of the EU ETS. Economic Modelling, 29(3), 884–892.
-
- Benz E, Trück S. Modeling the price dynamics of CO 2 emission allowances. Energy Economics. 2009;31(1):4–15. doi: 10.1016/j.eneco.2008.07.003. - DOI
-
- Byun SJ, Cho H. Forecasting carbon futures volatility using GARCH models with energy volatilities. Energy Economics. 2013;40:207–221. doi: 10.1016/j.eneco.2013.06.017. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
