Classifier Fusion for Detection of COVID-19 from CT Scans
- PMID: 35002014
- PMCID: PMC8722646
- DOI: 10.1007/s00034-021-01939-8
Classifier Fusion for Detection of COVID-19 from CT Scans
Abstract
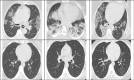
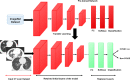
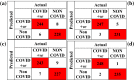
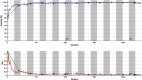
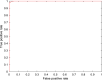
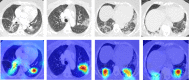
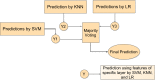
The coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is an infectious disease caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus. COVID-19 is found to be the most infectious disease in last few decades. This disease has infected millions of people worldwide. The inadequate availability and the limited sensitivity of the testing kits have motivated the clinicians and the scientist to use Computer Tomography (CT) scans to screen COVID-19. Recent advances in technology and the availability of deep learning approaches have proved to be very promising in detecting COVID-19 with increased accuracy. However, deep learning approaches require a huge labeled training dataset, and the current availability of benchmark COVID-19 data is still small. For the limited training data scenario, the CNN usually overfits after several iterations. Hence, in this work, we have investigated different pre-trained network architectures with transfer learning for COVID-19 detection that can work even on a small medical imaging dataset. Various variants of the pre-trained ResNet model, namely ResNet18, ResNet50, and ResNet101, are investigated in the current paper for the detection of COVID-19. The experimental results reveal that transfer learned ResNet50 model outperformed other models by achieving a recall of 98.80% and an F1-score of 98.41%. To further improvise the results, the activations from different layers of best performing model are also explored for the detection using the support vector machine, logistic regression and K-nearest neighbor classifiers. Moreover, a classifier fusion strategy is also proposed that fuses the predictions from the different classifiers via majority voting. Experimental results reveal that via using learned image features and classification fusion strategy, the recall, and F1-score have improvised to 99.20% and 99.40%.
Keywords: Activations; COVID-19; CT images; Classifier fusion; Diagnosis; Transfer learning.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
COVID-19 detection in CT and CXR images using deep learning models.Biogerontology. 2022 Feb;23(1):65-84. doi: 10.1007/s10522-021-09946-7. Epub 2022 Jan 22. Biogerontology. 2022. PMID: 35064446 Free PMC article.
-
Deep convolutional neural networks for COVID-19 automatic diagnosis.Microsc Res Tech. 2021 Nov;84(11):2504-2516. doi: 10.1002/jemt.23713. Epub 2021 Jun 14. Microsc Res Tech. 2021. PMID: 34121273 Free PMC article.
-
Transfer learning-based ensemble support vector machine model for automated COVID-19 detection using lung computerized tomography scan data.Med Biol Eng Comput. 2021 Apr;59(4):825-839. doi: 10.1007/s11517-020-02299-2. Epub 2021 Mar 18. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2021. PMID: 33738639 Free PMC article.
-
Deep transfer learning-based automated detection of COVID-19 from lung CT scan slices.Appl Intell (Dordr). 2021;51(1):571-585. doi: 10.1007/s10489-020-01826-w. Epub 2020 Aug 21. Appl Intell (Dordr). 2021. PMID: 34764547 Free PMC article.
-
Biphasic majority voting-based comparative COVID-19 diagnosis using chest X-ray images.Expert Syst Appl. 2023 Apr 15;216:119430. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2022.119430. Epub 2022 Dec 21. Expert Syst Appl. 2023. PMID: 36570382 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A fuzzy fine-tuned model for COVID-19 diagnosis.Comput Biol Med. 2023 Feb;153:106483. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.106483. Epub 2023 Jan 4. Comput Biol Med. 2023. PMID: 36621192 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Review of Machine Learning Used to Combat COVID-19.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Jul 31;12(8):1853. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12081853. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36010204 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A deep transfer learning-based convolution neural network model for COVID-19 detection using computed tomography scan images for medical applications.Adv Eng Softw. 2023 Jan;175:103317. doi: 10.1016/j.advengsoft.2022.103317. Epub 2022 Oct 24. Adv Eng Softw. 2023. PMID: 36311489 Free PMC article.
-
A deep learning-based method for pediatric congenital heart disease detection with seven standard views in echocardiography.World J Pediatr Surg. 2023 Jun 5;6(3):e000580. doi: 10.1136/wjps-2023-000580. eCollection 2023. World J Pediatr Surg. 2023. PMID: 37303480 Free PMC article.
-
Deep learning models-based CT-scan image classification for automated screening of COVID-19.Biomed Signal Process Control. 2023 Feb;80:104268. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2022.104268. Epub 2022 Sep 30. Biomed Signal Process Control. 2023. PMID: 36267466 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bishop CM. Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning. Berlin: Springer; 2006.
-
- Choe J, Lee SM, Do K-H, Lee G, Lee J-G, Lee SM, Seo JB. Deep learning–based image conversion of CT Reconstruction Kernels Improves Radiomics Reproducibility For Pulmonary Nodules Or Masses. Radiology. 2019;292(2):365–373. - PubMed
-
- Cover T, Hart P. Nearest neighbor pattern classification. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory. 1967;13(1):21–27.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
