Evidences and perspectives of the use of probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics, and postbiotics as adjuvants for prevention and treatment of COVID-19: A bibliometric analysis and systematic review
- PMID: 35002079
- PMCID: PMC8720301
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tifs.2021.12.033
Evidences and perspectives of the use of probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics, and postbiotics as adjuvants for prevention and treatment of COVID-19: A bibliometric analysis and systematic review
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to 'Evidences and perspectives of the use of probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics, and postbiotics as adjuvants for prevention and treatment of COVID-19: A bibliometric analysis and integrative review' [Trends in Food Science & Technology 120 (2022) 174-192].Trends Food Sci Technol. 2022 Mar;121:156-160. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2022.01.028. Epub 2022 Jan 31. Trends Food Sci Technol. 2022. PMID: 35125655 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19) is an infectious disease transmitted by the virus responsible for the severe acute respiratory syndrome 2 (SARS-CoV-2), which exhibit several clinical manifestations including gastrointestinal symptoms.
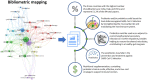
Scope and approach: This review aimed to provide insights and perspectives for the use of probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics, and postbiotics as adjuvants for prevention/treatment and/or modulation of the microbiota in COVID-19 patients. Eighty-four studies published in the Scopus database from the onset of the pandemic until December 2021 were assessed and submitted to a bibliometric analysis adapted from VOSviewer software.
Key findings and conclusions: Through bibliometric analysis, it might be suggested that the modulation of the gut/lung microbiome is promising as an adjuvant for the prevention/treatment of COVID-19 patients, due to immunomodulation properties related to probiotics and prebiotics. So far, few clinical studies involving the application of probiotics in COVID-19 patients have been completed, but reduction in the duration of the disease and the severity of symptoms as fatigue, olfactory dysfunction and breathlessness, nausea and vomiting and other gastrointestinal symptoms were some of the main findings. However, probiotics are not recommended to immunocompromised patients in corticosteroid therapy. The future perspectives point to the modulation of the intestinal microbiota by probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics, and postbiotics represent a promising adjuvant approach for improving the health of patients with COVID-19.
Keywords: Diet; Functional foods; Gut-lung axis; Immunomodulation; Microbiome; Pandemic.
© 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare to have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Probiotics, Prebiotics, Synbiotics, Postbiotics, and Obesity: Current Evidence, Controversies, and Perspectives.Curr Obes Rep. 2020 Sep;9(3):179-192. doi: 10.1007/s13679-020-00379-w. Curr Obes Rep. 2020. PMID: 32472285 Review.
-
Effects and Mechanisms of Probiotics, Prebiotics, Synbiotics, and Postbiotics on Metabolic Diseases Targeting Gut Microbiota: A Narrative Review.Nutrients. 2021 Sep 15;13(9):3211. doi: 10.3390/nu13093211. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34579087 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the Potential Use of Probiotics, Prebiotics, Synbiotics, and Postbiotics as Adjuvants for Modulating the Vaginal Microbiome: a Bibliometric Review.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2025 Jan 17. doi: 10.1007/s12602-024-10444-8. Online ahead of print. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2025. PMID: 39821884 Review.
-
Gut microbiome modulation by probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics and postbiotics: a novel strategy in food allergy prevention and treatment.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2024;64(17):5984-6000. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2022.2160962. Epub 2022 Dec 28. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 36576159 Review.
-
Probiotics/Prebiotics in Viral Respiratory Infections: Implication for Emerging Pathogens.Recent Pat Biotechnol. 2021 Oct 4;15(2):112-136. doi: 10.2174/1872208315666210419103742. Recent Pat Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33874878 Review.
Cited by
-
Cardiopulmonary exercise test: A 20-year (2002-2021) bibliometric analysis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Aug 15;9:982351. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.982351. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 36046187 Free PMC article.
-
The dynamic linkage between covid-19 and nutrition: a review from a probiotics perspective using machine learning and bibliometric analysis.Front Nutr. 2025 May 9;12:1575130. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1575130. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40416372 Free PMC article.
-
Gut microbiota composition is altered in postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome and post-acute COVID-19 syndrome.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 9;14(1):3389. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-53784-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38336892 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations in microbiota of patients with COVID-19: implications for therapeutic interventions.MedComm (2020). 2024 Mar 15;5(4):e513. doi: 10.1002/mco2.513. eCollection 2024 Apr. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 38495122 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Uncovering the Probiotic Supplement Landscape: Market Offerings, Sales Patterns, and Future Forecasts Using Machine Learning Approach - A Case Study of Montenegro.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2024 Nov 25. doi: 10.1007/s12602-024-10400-6. Online ahead of print. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2024. PMID: 39581930
References
-
- d'Ettorre G., Ceccarelli G., Marazzato M., Campagna G., Pinacchio C., Alessandri F., et al. Challenges in the management of SARS-CoV2 infection: The role of oral bacteriotherapy as complementary therapeutic strategy to avoid the progression of COVID-19. Frontiers of Medicine. 2020;7:389. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2020.00389. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Al Noman A., Islam M.S., Sana S., Mondal P., Meem R.I., Rana S., et al. Correction to: A review of the genome, epidemiology, clinical features, prevention, and treatment scenario of COVID-19: Bangladesh aspects. The Egyptian Journal of Bronchology. 2021;15:8. doi: 10.1186/s43168-021-00057-y. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
