CNNM2 Heterozygous Variant Presenting as Hypomagnesemia and West Syndrome: Expanding the Spectrum of CNNM2 Gene-Related Epileptic Disorders
- PMID: 35002148
- PMCID: PMC8680880
- DOI: 10.4103/aian.AIAN_1130_20
CNNM2 Heterozygous Variant Presenting as Hypomagnesemia and West Syndrome: Expanding the Spectrum of CNNM2 Gene-Related Epileptic Disorders
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
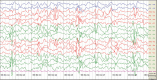
Figures

References
-
- Sharawat IK, Kasinathan A, Sahu JK, Sankhyan N. Response to carbamazepine in KCNQ2 related early infantile epileptic encephalopathy. Indian J Pediatr. 2019;86:301–2. - PubMed
-
- Sharawat IK, Yadav J, Saini L. Novel GRIN2B mutation: A rare cause of severe epileptic encephalopathy. Neurol India. 2019;67:562–3. - PubMed
-
- Sood A, Grover N, Sharma R. Biochemical abnormalities in neonatal seizures. Indian J Pediatr. 2003;70:221–4. - PubMed

