Inference for Batched Bandits
Abstract
As bandit algorithms are increasingly utilized in scientific studies and industrial applications, there is an associated increasing need for reliable inference methods based on the resulting adaptively-collected data. In this work, we develop methods for inference on data collected in batches using a bandit algorithm. We first prove that the ordinary least squares estimator (OLS), which is asymptotically normal on independently sampled data, is not asymptotically normal on data collected using standard bandit algorithms when there is no unique optimal arm. This asymptotic non-normality result implies that the naive assumption that the OLS estimator is approximately normal can lead to Type-1 error inflation and confidence intervals with below-nominal coverage probabilities. Second, we introduce the Batched OLS estimator (BOLS) that we prove is (1) asymptotically normal on data collected from both multi-arm and contextual bandits and (2) robust to non-stationarity in the baseline reward.
Figures
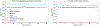
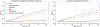
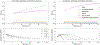
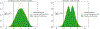
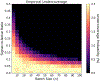

References
-
- Abbasi-Yadkori Yasin, Pál Dávid, and Szepesvári Csaba. Improved algorithms for linear stochastic bandits. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pages 2312–2320, 2011.
-
- Agarwal Arpit, Agarwal Shivani, Assadi Sepehr, and Khanna Sanjeev. Learning with limited rounds of adaptivity: Coin tossing, multi-armed bandits, and ranking from pairwise comparisons. In Conference on Learning Theory, pages 39–75, 2017.
-
- Amemiya Takeshi. Advanced Econometrics. Harvard University Press, 1985.
-
- Brannath W, Gutjahr G, and Bauer P. Probabilistic foundation of confirmatory adaptive designs. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 107(498):824–832, 2012.
-
- Deshpande Yash, Javanmard Adel, and Mehrabi Mohammad. Online debiasing for adaptively collected high-dimensional data. arXiv preprint arXiv:1911.01040, 2019.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
