Recent Advances in the Clinical Value and Potential of Dexmedetomidine
- PMID: 35002284
- PMCID: PMC8724687
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S346089
Recent Advances in the Clinical Value and Potential of Dexmedetomidine
Abstract
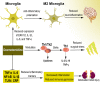
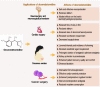
Dexmedetomidine, a highly selective α2-adrenoceptor agonist, has sedative, anxiolytic, analgesic, sympatholytic, and opioid-sparing properties and induces a unique sedative response which shows an easy transition from sleep to wakefulness, thus allowing a patient to be cooperative and communicative when stimulated. Recent studies indicate several emerging clinical applications via different routes. We review recent data on dexmedetomidine studies, particularly exploring the varying routes of administration, experimental implications, clinical effects, and comparative advantages over other drugs. A search was conducted on the PubMed and Web of Science libraries for recent studies using different combinations of the words "dexmedetomidine", "route of administration", and pharmacological effect. The current routes, pharmacological effects, and application categories of dexmedetomidine are presented. It functions by stimulating pre- and post-synaptic α2-adrenoreceptors within the central nervous system, leading to hyperpolarization of noradrenergic neurons, induction of an inhibitory feedback loop, and reduction of norepinephrine secretion, causing a sympatholytic effect, in addition to its anti-inflammation, sleep induction, bowel recovery, and sore throat reduction effects. Compared with similar α2-adrenoceptor agonists, dexmedetomidine has both pharmacodynamics advantage of a significantly greater α2:α1-adrenoceptor affinity ratio and a pharmacokinetic advantage of having a significantly shorter elimination half-life. In its clinical application, dexmedetomidine has been reported to present a significant number of benefits including safe sedation for various surgical interventions, improvement of intraoperative and postoperative analgesia, sedation for compromised airways without respiratory depression, nephroprotection and stability of hypotensive hemodynamics, reduction of postoperative nausea and vomiting and postoperative shivering incidence, and decrease of intraoperative blood loss. Although the clinical application of dexmedetomidine is promising, it is still limited and further research is required to enhance understanding of its pharmacological properties, patient selection, dosage, and adverse effects.
Keywords: analgesic; anesthesia; anti-inflammation; dexmedetomidine; sedation; surgery.
© 2021 Liu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

