The Lactate/Albumin Ratio Predicts Mortality in Critically Ill Patients with Acute Kidney Injury: An Observational Multicenter Study on the eICU Database
- PMID: 35002307
- PMCID: PMC8722580
- DOI: 10.2147/IJGM.S339767
The Lactate/Albumin Ratio Predicts Mortality in Critically Ill Patients with Acute Kidney Injury: An Observational Multicenter Study on the eICU Database
Abstract
Objective: The serum lactate/albumin ratio (LAR) can be used to independently predict mortality due to sepsis. However, whether the LAR predicts the outcomes of critically ill patients with acute kidney injury (AKI) remains unclear. This study was performed to assess the prognostic value of the LAR in critically ill AKI patients.
Methods: This retrospective observational study enrolled AKI patients, and all data were collected through the eICU Collaborative Research Database. Outcomes included in-hospital and intensive care unit (ICU) death. Multivariate Cox regression analysis was used to determine independent risk factors. Forest plots and smoothing curves were generated. A series of subgroup analyses were performed to further validate the robustness of the findings.
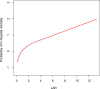
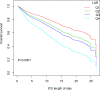
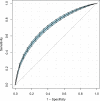
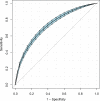
Results: A total of 4666 eligible patients were enrolled. We divided the participants into four groups according to the LAR: quartile (Q)1 (LAR < 0.46, n = 1167), Q2 (0.46 ≤ LAR < 0.79, n = 1162), Q3 (0.79 ≤ LAR < 1.49, n = 1170), and Q4 (LAR ≥ 1.49, n = 1167). The LAR, when analyzed as a continuous variable, was associated with hospital and ICU mortality (adjusted hazard ratio [HR] 1.22, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.18-1.26, P < 0.0001 for both). The risk of in-hospital and ICU mortality increased with increasing LAR Q relative to Q1. The smoothing curves revealed a continuous linear association after adjusting for all covariates. By the Kaplan-Meier analysis, patients in the higher LAR group showed significantly shorter survival time. By the receiver operating characteristic analysis, LAR was efficient in predicting in-hospital mortality (area under the curve [AUC]: 0.717) and ICU mortality (AUC: 0.733). A positive and consistent effect of the LAR was seen in all subgroups analyses after adjusting for all covariates.
Conclusion: A high LAR is an independent risk factor for in-hospital and ICU mortality in critically ill patients with AKI. Further prospective studies are needed to validate these result.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; critical care; lactate/albumin ratio; mortality.
© 2021 Zhu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Association between lactate/albumin ratio and 28-day all-cause mortality in critically ill patients with acute myocardial infarction.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 10;14(1):23677. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-73788-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39389996 Free PMC article.
-
The association between lactate dehydrogenase to serum albumin ratio and the 28-day mortality in patients with sepsis-associated acute kidney injury in intensive care: a retrospective cohort study.Ren Fail. 2023 Dec;45(1):2212080. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2023.2212080. Ren Fail. 2023. PMID: 37194715 Free PMC article.
-
Association between lactate to albumin ratio and mortality among sepsis associated acute kidney injury patients.BMC Infect Dis. 2025 Mar 26;25(1):414. doi: 10.1186/s12879-025-10838-1. BMC Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40140783 Free PMC article.
-
Association between lactate-to-albumin ratio and mortality in hepatic failure: a retrospective cohort study.BMC Infect Dis. 2025 Mar 28;25(1):433. doi: 10.1186/s12879-025-10783-z. BMC Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40155840 Free PMC article.
-
Lactate-to-Albumin Ratio (LAR) as a Predictor of All-Cause Mortality in Patients With Myocardial Infarction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cureus. 2025 Apr 13;17(4):e82166. doi: 10.7759/cureus.82166. eCollection 2025 Apr. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40364881 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of lactate/albumin ratio to lactate and lactate clearance for predicting outcomes in patients with septic shock admitted to intensive care unit: an observational study.Sci Rep. 2022 Jul 29;12(1):13047. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-14764-z. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35906231 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive accuracy of lactate albumin ratio for mortality in intensive care units: a nationwide cohort study.BMJ Open. 2024 Dec 20;14(12):e088926. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-088926. BMJ Open. 2024. PMID: 39806598 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis of Multiple Organ Dysfunction in Neonates with Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy: Vasoactive Inotropic Score, Renal Score, Fibrosis-5 Index and Lactate/Albumin Ratio.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Dec 12;14(24):2796. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14242796. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39767157 Free PMC article.
-
[ROC curves: general characteristics and their usefulness in clinical practice].Rev Med Inst Mex Seguro Soc. 2023 Oct 2;61(Suppl 3):S497-S502. doi: 10.5281/zenodo.8319791. Rev Med Inst Mex Seguro Soc. 2023. PMID: 37935015 Free PMC article. Spanish.
-
The relationship between lactate/albumin ratio and prognosis in children with acute kidney injury.PLoS One. 2025 Aug 1;20(8):e0329453. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0329453. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40748973 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

