Effect of transcranial magnetic stimulation on treatment effect and immune function
- PMID: 35002433
- PMCID: PMC8717157
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.08.104
Effect of transcranial magnetic stimulation on treatment effect and immune function
Abstract
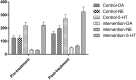
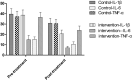
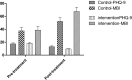
To explore the effect of transcranial stimulation on the therapeutic effect and immune function of patients with post-stroke depression (PSD). Methods Selection in September 2020-April 2021 on the diagnosis of 70 patients with PSD as the research object, 35 patients were randomly divided into control group and intervention group and control group given conventional treatment, the intervention group in the control group on the basis of the application of transcranial magnetic stimulation treatment, compare the curative effect of two groups of patients after the treatment cycle and the effects on the immune function. Results After treatment, the levels of DA, NE, 5-HT in 2 groups were significantly increased, and those in the observation group were significantly higher than those in the control group (P < 0.05). After 8 weeks of treatment, serum Gly content in 2 groups was significantly increased and Glu content was significantly decreased compared with before treatment. Compared with the control group, serum Gly content in observation group was significantly increased and Glu content was significantly decreased after treatment (P < 0.05). After 8 weeks of treatment, the contents of IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α in serum of 2 groups were significantly decreased, compared with the control group, the contents of IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α in serum of observation group were significantly decreased (P < 0.05); Before treatment, there was no significant difference in PHQ-9 score and MBI score between the two groups (P > 0.05). After 8 weeks of treatment, PHQ-9 score and MBI score in the two groups were better than before treatment, and the observation group was better than the control group (P < 0.05). Conclusion Transcranial magnetic stimulation therapy can not only effectively promote the synthesis and release of monoamine neurotransmitters in patients with post-stroke depression, regulate the inhibitory/excitatory amino acid neurotransmitters, reduce inflammatory response, improve the clinical treatment effect and enhance the immune function of PSD patients, which has clinical application value.
Keywords: Poststroke depression; The immune function; The neurotransmitter; Transcranial magnetic stimulation.
© 2021 Published by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of King Saud University.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous