Exploring the role of cathepsin in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 35002435
- PMCID: PMC8716961
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.09.014
Exploring the role of cathepsin in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
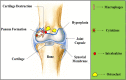
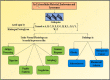
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory disease which is marked by leukocytes infiltration inside synovial tissue, joints and also inside synovial fluid which causes progressive destruction of joint cartilage. There are numerous genetical and lifestyle factors, responsible for rheumatoid arthritis. One such factor can be cysteine cathepsins, which act as proteolytic enzymes. These proteolytic enzyme gets activated at acidic pH and are found in lysosomes and are also termed as cysteine proteases. These proteases belong to papain family and have their elucidated role in musculoskeletal disorders. Numerous cathepsins have their targeted role in rheumatoid arthritis. These proteases are secreted through various cell types which includes matrix metalloproteases and papain like cysteine proteases. These proteases can potentially lead to bone and cartilage destruction which causes an immune response in case of inflammatory arthritis.
Keywords: Cathepsin; Cysteine protease; Inflammation; Matrix-metalloprotease; Rheumatoid arthritis.
© 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of King Saud University.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Expression and activity profiling of selected cysteine cathepsins and matrix metalloproteinases in synovial fluids from patients with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis.Biol Chem. 2010 May;391(5):571-9. doi: 10.1515/BC.2010.035. Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20180636
-
Role of cathepsin K in normal joints and in the development of arthritis.Curr Drug Targets. 2007 Feb;8(2):315-23. doi: 10.2174/138945007779940188. Curr Drug Targets. 2007. PMID: 17305509 Review.
-
Cathepsin B in synovial cells at the site of joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Nov;34(11):1444-51. doi: 10.1002/art.1780341116. Arthritis Rheum. 1991. PMID: 1953821
-
Expression of the collagenolytic and Ras-induced cysteine proteinase cathepsin L and proliferation-associated oncogenes in synovial cells of MRL/I mice and patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Matrix. 1990 Dec;10(6):349-61. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8832(11)80142-3. Matrix. 1990. PMID: 2084514
-
The role of cathepsins in osteoporosis and arthritis: rationale for the design of new therapeutics.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2005 May 25;57(7):973-93. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2004.12.013. Epub 2005 Apr 15. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2005. PMID: 15876399 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanistic role of quercetin as inhibitor for adenosine deaminase enzyme in rheumatoid arthritis: systematic review.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024 Jan 16;29(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s11658-024-00531-7. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024. PMID: 38225555 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of key biomarkers for predicting CAD progression in inflammatory bowel disease via machine-learning and bioinformatics strategies.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Mar;28(6):e18175. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18175. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38451044 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-inflammatory and anti-arthritic activities of ethanolic extract of Myxopyrum serratulum A.W. Hill.Lab Anim Res. 2024 Sep 26;40(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s42826-024-00220-8. Lab Anim Res. 2024. PMID: 39327635 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Proteomics of the Acanthopagrus schlegelii Gonad in Different Sex Reversal.Genes (Basel). 2022 Jan 28;13(2):253. doi: 10.3390/genes13020253. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35205296 Free PMC article.
-
Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking and in vivo-based Analysis on the Effects of the MBZM-N-IBT for Arthritis.Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2025;21(2):194-210. doi: 10.2174/0115734099307360240731052835. Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2025. PMID: 39108124
References
-
- Ahmed N.K., Watts L., Palmer J., Thornburg L., Prior J., Esser R. Peptidyl fluoromethyl ketones as inhibitors of cathepsin B: implication for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1992;44(6):12210–12217. - PubMed
-
- Arora, M., Pandey, G., Chauhan, S.S., 2021. Cysteine Cathepsins and Their Prognostic and Therapeutic Relevance in Leukemia, Annals of the National Academy of Medical Sciences (India).
-
- Asagiri M., Hirai T., Kunigami T., Kamano S., Gober H.-J., Okamoto K., Nishikawa K., Latz E., Golenbock D.T., Aoki K., Ohya K., Imai Y., Morishita Y., Miyazono K., Kato S., Saftig P., Takayanagi H. Cathepsin K-dependent toll-like receptor 9 signaling revealed in experimental arthritis. Science. 2008;319(5863):624–627. - PubMed
-
- Bali, J., Cousse, H., Neuzil, E., 2001. Biochemical basis of the pharmacologic action of chondroitin sulfates on the osteoarticular system, InSeminars in arthritis and rheumatism, Vol. 31, no. 1, pp. 58–68. WB Saunders. - PubMed
-
- Barrett A., Davies M., Grubb A. The place of human γ-trace (cystatin C) amongst the cysteine proteinase inhibitors. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1984;120(2):631–636. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

