Hepatoprotective effects of methanolic extract of green tea against Thioacetamide-Induced liver injury in Sprague Dawley rats
- PMID: 35002452
- PMCID: PMC8716963
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.09.023
Hepatoprotective effects of methanolic extract of green tea against Thioacetamide-Induced liver injury in Sprague Dawley rats
Abstract
Ethnopharmacological relevance: Since ancient times, herbal medicines have been applied in the treatment of cancer. Tea, derivative from the dried leaves of Camellia sinensis (L.) Kuntze plant is the most popular beverage globally after water and is available in various forms. Green tea has been expansively investigated for its beneficial properties of cancer prevention and therapy. The goal of the research: The current study was conducted to evaluate the hepaprotective character of methanolic green tea extract and its mechanism of action contrary to thioacetamide (TAA)-produced liver fibrosis of Sprague Dawley rats.
Materials and methods: Thirty rodents were equally placed in 5 clusters including normal control, TAA group as a positive control, silymarin as standard drug control, and treatment groups consisting of high dose and a low dose Camellia sinensis. Rats in experimental clusters by mouth fed with C. sinensis at 250 mg/kg or 500 mg/kg daily for 2 months. After 60 days, all rats were sacrificed. Blood specimens were gathered for liver biochemical examination. Livers of all groups were dissected out and subjected to histopathological examination through the Hematoxylin and Eosin stain, Masson trichrome, and immunohistochemistry stains (PCNA). Liver tissue homogenate was also analyzed for antioxidant activity parameters.
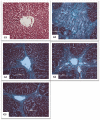
Results: Gross morphological examination showed a regular liver architecture in C. sinensis fed collections compared to the TAA sets. Histology of rat's liver fed with C. sinensis showed an important decrease in the liver index with hepatic cells propagation, mild cellular injury, and immunostaining showed significant down-expression of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA). TAA produced liver fibrosis through a significant increase in serum alanine transferase, aspartate aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase, and bilirubin. Total protein and albumin also decreased in the TAA group. Moreover, the reduction of antioxidant enzyme activity including superoxide dismutase and catalase as well as the increase in malondialdehyde was detected in the TAA control group. Meanwhile, an abnormal level of liver biochemical parameters was restored closer to the normal levels in serum of the C. sinensis-fed clusters. In addition, C. sinensis fed assemblies showed elevated antioxidative enzymes activity with a reduction in malondialdehyde level comparable to the levels in silymarin-treated rats.
Conclusions: Green tea potentially inhibited the progression of liver cirrhosis, down -regulation of PCNA proliferation, prevented oxidation of hepatocytes, recovered SOD and CAT enzymes, condensed MDA and reduced cellular inflammation.
Keywords: Green Tea; Hepatoprotective; Histopathology; Immunohistochemistry; Liver cirrhosis; Silymarin; Thioacetamide.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Abd Eldaim M.A., Tousson E., Soliman M.M., El Sayed I.E.T., Aleem A.A.H.A., Elsharkawy H.N. Grape seed extract ameliorated Ehrlich solid tumor-induced hepatic tissue and DNA damage with reduction of PCNA and P53 protein expression in mice. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021:1–13. - PubMed
-
- Abood W.N., Bradosty S.W., Shaikh F.K., Salehen N.A., Farghadani R., Agha N.F.S., Al-Medhtiy M.H., Kamil T.D.A., Agha A.S., Abdulla M.A. Garcinia mangostana peel extracts exhibit hepatoprotective activity against thioacetamide-induced liver cirrhosis in rats. J. Funct. Foods. 2020;74
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

