Cytokine storm in COVID-19: from viral infection to immune responses, diagnosis and therapy
- PMID: 35002503
- PMCID: PMC8741849
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.59272
Cytokine storm in COVID-19: from viral infection to immune responses, diagnosis and therapy
Abstract
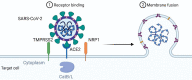
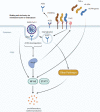
The COVID-19 outbreak is emerging as a significant public health challenge. Excessive production of proinflammatory cytokines, also known as cytokine storm, is a severe clinical syndrome known to develop as a complication of infectious or inflammatory diseases. Clinical evidence suggests that the occurrence of cytokine storm in severe acute respiratory syndrome secondary to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection is closely associated with the rapid deterioration and high mortality of severe cases. In this review, we aim to summarize the mechanism of SARS-CoV-2 infection and the subsequent immunological events related to excessive cytokine production and inflammatory responses associated with ACE2-AngII signaling. An overview of the diagnosis and an update on current therapeutic regimens and vaccinations is also provided.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; cytokine storm; cytokines; diagnosis; immune response; therapy; vaccination.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of sEH inhibition on the eicosanoid and cytokine storms in SARS-CoV-2-infected mice.FASEB J. 2024 May 31;38(10):e23692. doi: 10.1096/fj.202302202RR. FASEB J. 2024. PMID: 38786655 Free PMC article.
-
An enlightening role for cytokine storm in coronavirus infection.Clin Immunol. 2021 Jan;222:108615. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2020.108615. Epub 2020 Oct 23. Clin Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33203513 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The potential for Lactoferrin to reduce SARS-CoV-2 induced cytokine storm.Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 Jun;95:107571. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107571. Epub 2021 Mar 12. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33765614 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Critical Determinants of Cytokine Storm and Type I Interferon Response in COVID-19 Pathogenesis.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2021 May 12;34(3):e00299-20. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00299-20. Print 2021 Jun 16. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2021. PMID: 33980688 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Capturing Cytokines with Advanced Materials: A Potential Strategy to Tackle COVID-19 Cytokine Storm.Adv Mater. 2021 May;33(20):e2100012. doi: 10.1002/adma.202100012. Epub 2021 Apr 10. Adv Mater. 2021. PMID: 33837596 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Potential effects of icariin, the Epimedium-derived bioactive compound in the treatment of COVID-19: a hypothesis.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2022 Sep;395(9):1019-1027. doi: 10.1007/s00210-022-02262-y. Epub 2022 Jun 3. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35657423 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential biomarkers for fatal outcome prognosis in a cohort of hospitalized COVID-19 patients with pre-existing comorbidities.Clin Transl Sci. 2023 Dec;16(12):2687-2699. doi: 10.1111/cts.13663. Epub 2023 Nov 9. Clin Transl Sci. 2023. PMID: 37873554 Free PMC article.
-
Enpatoran in COVID-19 pneumonia: Safety and efficacy results from a phase II randomized trial.Clin Transl Sci. 2023 Dec;16(12):2640-2653. doi: 10.1111/cts.13658. Epub 2023 Oct 23. Clin Transl Sci. 2023. PMID: 37873555 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Cytokine profiles of mild-to-moderate SARS-CoV-2 infected and recovered pre-vaccinated individuals residing in Indonesia.PeerJ. 2024 Apr 18;12:e17257. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17257. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 38646483 Free PMC article.
-
Risk for postpartum depressive symptoms among pregnant women in a tertiary care setting with and without a positive COVID-19 test.Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2022 Nov-Dec;79:1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2022.08.006. Epub 2022 Sep 6. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 36108453 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Drosten C, Gunther S, Preiser W, van der Werf S, Brodt HR, Becker S. et al. Identification of a novel coronavirus in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1967–76. - PubMed
-
- Zaki AM, van Boheemen S, Bestebroer TM, Osterhaus AD, Fouchier RA. Isolation of a novel coronavirus from a man with pneumonia in Saudi Arabia. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:1814–20. - PubMed
-
- Data OWi. Coronavirus (COVID-19) Vaccinations. https://ourworldindata.org/covid-vaccination.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

